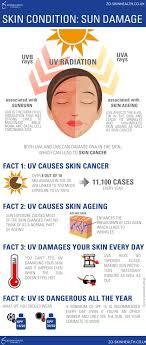
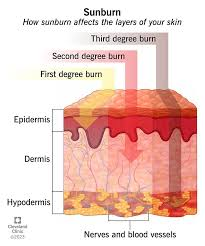
Sun damage to the skin can manifest as sunburn, premature aging (wrinkles, fine lines, and age spots), and an increased risk of skin cancer. While it’s essential to practice sun protection to prevent further damage, there are also ways to treat existing sun damage.

Treatment for sun damage are:-
1. Topical Treatments: (i)Retinoids:Retinoids are a class of compounds derived from vitamin A that play a crucial role in various physiological processes, including skin health. They are widely used in dermatology and skincare for their ability to improve skin texture, reduce the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles, and promote overall skin renewal.
Types of Retinoids:-
- Retinol: Available over the counter in many skincare products. It undergoes conversion in the skin to its active form, retinoic acid.
- Retinaldehyde: Intermediate between retinol and retinoic acid.
- Retinoic Acid (Tretinoin): Available as a prescription-strength topical treatment.
Retinoids Work:-
- Retinoids work by binding to specific receptors in the skin. Once applied, they promote cell turnover and stimulate the production of new skin cells.
- They can improve the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles, reduce hyperpigmentation, and enhance skin elasticity.
Use in Skincare:–
- Retinoids are commonly found in prescription creams, gels, and lotions, as well as over-the-counter skincare products.
- Start with a lower concentration if you’re new to retinoids to allow your skin to adjust, and gradually increase as tolerated.
- It’s essential to use sunscreen when using retinoids, as they can increase sensitivity to UV radiation.
(ii) Topical antioxidants: Topical antioxidants are substances applied to the skin to help neutralize free radicals and protect the skin from oxidative stress caused by factors like sun exposure, pollution, and environmental damage. Free radicals are unstable molecules that can damage skin cells and contribute to signs of aging, including wrinkles and fine lines. Topical antioxidants work by scavenging these free radicals, helping to maintain skin health.
Topical antioxidants used in skincare:-
Vitamin C (Ascorbic Acid):
- One of the most well-known antioxidants in skincare.
- Helps brighten the skin, reduce hyperpigmentation, and stimulate collagen production.
- Effective against free radicals caused by UV exposure.
Vitamin E (Tocopherol):
- An antioxidant that works synergistically with vitamin C.
- Helps protect the skin barrier and maintain skin hydration.
- Often used in combination with other antioxidants for enhanced efficacy.
Ferulic Acid:
- Often combined with vitamins C and E to boost their stability and effectiveness.
- Provides additional protection against UV damage.
Resveratrol:
- Found in red grapes, red wine, and some berries.
- Known for its anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties.
- Helps neutralize free radicals and may promote collagen production.
Green Tea Extract:
- Contains polyphenols, particularly epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG).
- Possesses antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties.
- Helps protect against UV damage and reduce redness.
Coenzyme Q10 (Ubiquinone):
- Naturally present in the body, it helps produce energy in cells.
- Acts as an antioxidant, protecting the skin from oxidative stress.
- May help reduce the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles.
Niacinamide (Vitamin B3):
- Has antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties.
- Supports the skin barrier and helps even out skin tone.
- Suitable for sensitive skin.
Alpha Lipoic Acid:
- Both water- and fat-soluble, making it versatile in protecting against free radicals.
- Helps improve the appearance of fine lines and skin texture.
Selenium:
- A trace element with antioxidant properties.
- Supports the skin’s natural defense mechanisms against oxidative stress.
Zinc:
- An essential mineral with antioxidant properties.
- Supports wound healing and may help soothe irritated skin.
(iii)Alpha hydroxy acids (AHAs) and beta hydroxy acids (BHAs):Alpha hydroxy acids (AHAs) and beta hydroxy acids (BHAs) are chemical exfoliants that are commonly used in skincare to improve the texture and appearance of the skin.
Alpha Hydroxy Acids (AHAs):
Benefits:
- Smoothing and improving skin texture.
- Reducing the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles.
- Brightening the skin and addressing hyperpigmentation.
- Enhancing the effectiveness of other skincare products.
Beta Hydroxy Acids (BHAs):
Benefits:
- Treating acne and preventing breakouts.
- Reducing inflammation and redness.
- Exfoliating within the pores, making them suitable for addressing blackheads and whiteheads.
- Improving skin texture and tone.
2. Chemical Peels: Chemical peels are cosmetic treatments that involve the application of a chemical solution to the skin, causing it to exfoliate and eventually peel off. The goal of a chemical peel is to remove the outer layers of damaged skin, revealing smoother, more even-toned skin underneath. Chemical peels can be used to address various skin concerns and are typically performed by dermatologists or trained skincare professionals.
Conditions Treated with Chemical Peels:-
- Fine Lines and Wrinkles: Chemical peels can improve the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles, particularly on the face.
- Sun Damage: Peels can help reduce the effects of sun damage, including pigmentation irregularities and sunspots.
- Acne Scars: Chemical peels can improve the texture of the skin and reduce the appearance of acne scars.
- Uneven Skin Tone: Peels can address uneven skin tone caused by factors like age spots, melasma, or post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation.
- Texture Irregularities: Peels can improve skin texture by promoting cell turnover and collagen production.
3. Laser Therapy: Laser therapy, or laser skin resurfacing, is a cosmetic procedure that uses focused beams of light to treat various skin issues. The laser light is targeted at specific areas of the skin, and it can be adjusted in terms of intensity, wavelength, and duration, making it a versatile tool for addressing different skin concerns. Laser therapy is typically performed by dermatologists or trained skincare professionals.

Conditions Treated with Laser Therapy:–
- Wrinkles and Fine Lines: Laser therapy can improve the appearance of wrinkles and fine lines by stimulating collagen production and promoting skin tightening.
- Scars: Both acne scars and surgical scars can be treated with laser therapy to improve texture and reduce visibility.
- Hyperpigmentation: Lasers can target excess pigmentation, such as sunspots, age spots, and melasma.
- Vascular Lesions: Certain lasers can target blood vessels, reducing the appearance of spider veins, broken blood vessels, and other vascular lesions.
- Hair Removal: Laser hair removal is a common application, targeting hair follicles to reduce or eliminate hair growth in specific areas.
4. Microdermabrasion: Microdermabrasion is a non-invasive cosmetic procedure that uses a mechanical exfoliation technique to remove the outermost layer of dead skin cells from the surface of the skin. This procedure aims to improve skin texture, reduce the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles, and promote a more even skin tone. Microdermabrasion is typically performed by dermatologists, estheticians, or skincare professionals.
Conditions Treated with Microdermabrasion:-
- Dull Skin: Microdermabrasion can provide an instant brightening effect by removing dead skin cells and promoting cell turnover.
- Fine Lines and Wrinkles: By stimulating collagen production and improving skin texture, microdermabrasion may reduce the appearance of fine lines.
- Mild Acne Scars: It can help improve the texture of the skin and reduce the visibility of certain types of acne scars.
- Uneven Skin Tone: Microdermabrasion can address hyperpigmentation and promote a more even skin tone.
- Enlarged Pores: While it doesn’t change the size of pores, microdermabrasion can improve their appearance by removing excess oil and debris.
5. Prescription Medications:rescription medications for skincare are commonly used to address various dermatological conditions and concerns. Dermatologists may prescribe medications to treat acne, hyperpigmentation, psoriasis, eczema, rosacea, and other skin-related issues.
6. Moisturize:Moisturizing is a crucial step in skincare that involves applying a product to the skin to help maintain its hydration and prevent dryness. Regardless of your skin type, moisturizing is an essential component of a healthy skincare routine.
7. Sunscreen: Sunscreen is a crucial component of a skincare routine and plays a vital role in protecting the skin from the harmful effects of ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun. UV radiation can cause sunburn, premature aging, and increase the risk of skin cancer.
8. Hydration and Nutrition: Hydration and nutrition play crucial roles in maintaining overall health, including the health of your skin. Both factors contribute to the appearance, resilience, and function of the skin.
Hydration:Antioxidants: A diet rich in antioxidants, found in fruits and vegetables, helps protect the skin from oxidative stress caused by free radicals. This can contribute to a healthier and more radiant complexion.
Nutrition: Nutrients like vitamins A, C, and E, as well as minerals like zinc and selenium, play crucial roles in skin health. They support collagen production, help maintain skin structure, and promote wound healing.
9. Consult a Dermatologist: Consulting with a dermatologist is important for maintaining the health of your skin and addressing any specific concerns or conditions you may have. Dermatologists are medical professionals specializing in the diagnosis and treatment of skin, hair, and nail conditions.