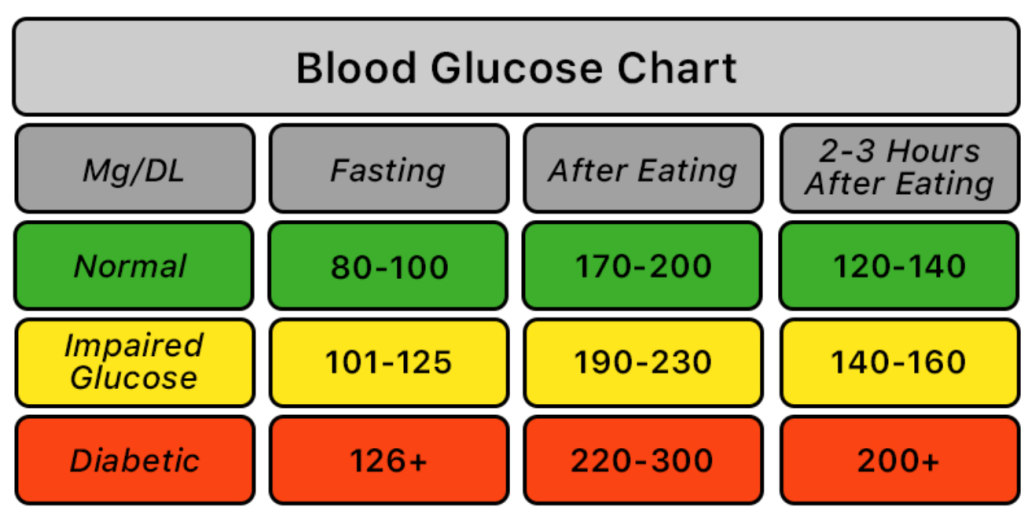
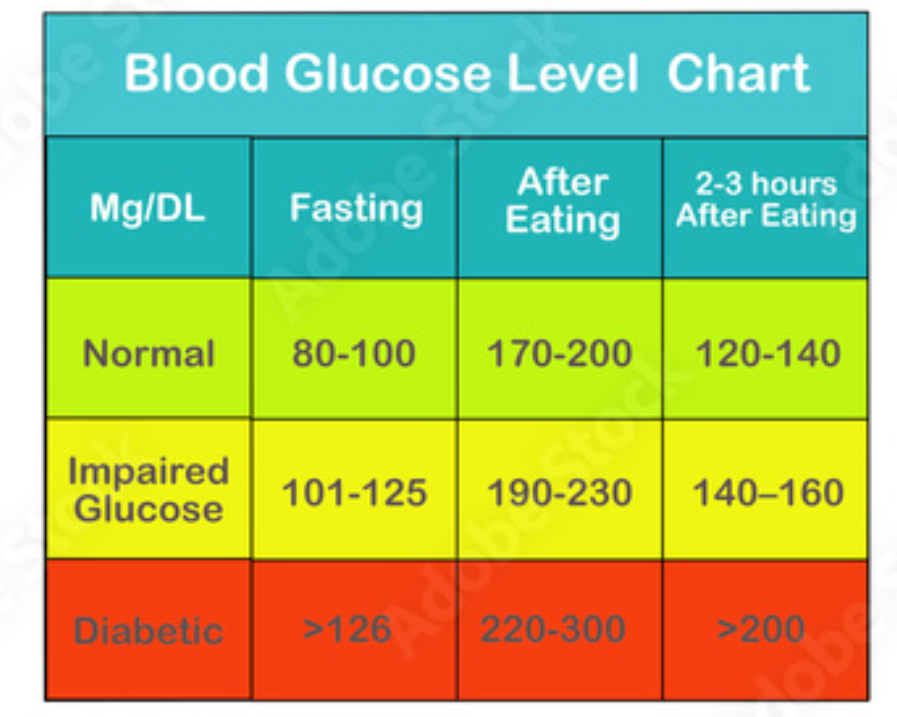
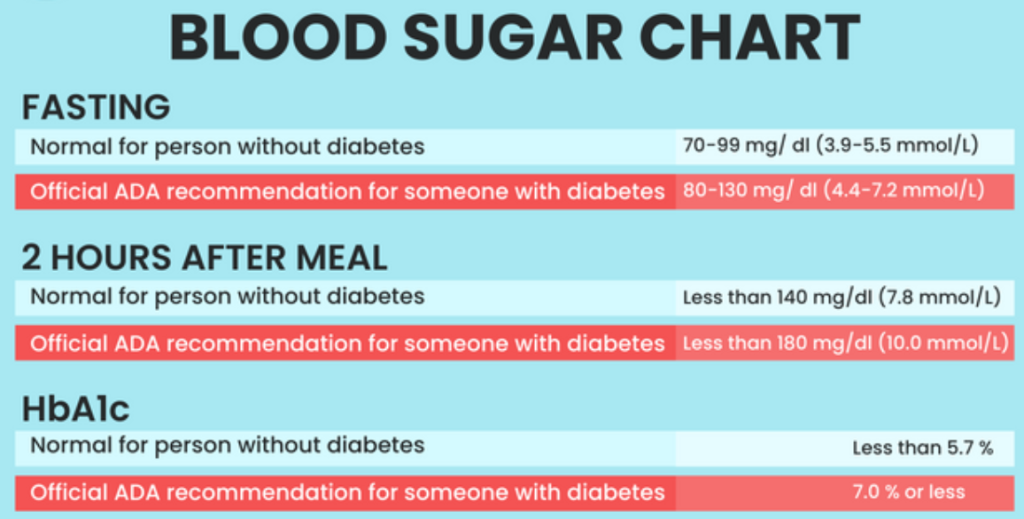
Here is a blood sugar level chart for diabetics:
| Time of Day | Normal Blood Sugar Level (mg/dL) | Prediabetes Blood Sugar Level (mg/dL) | Diabetic Blood Sugar Level (mg/dL) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fasting (8-12 hours after eating) | 70-99 | 100-125 | 126 or higher |
| Before meals | 70-130 | 140-199 | 200 or higher |
| 1 hour after meals | 90-140 | 140-199 | Less than 180 |
| 2 hours after meals | Less than 120 | Less than 160 | Less than 150 |
| Bedtime | 90-150 | 140-199 | 90-150 |
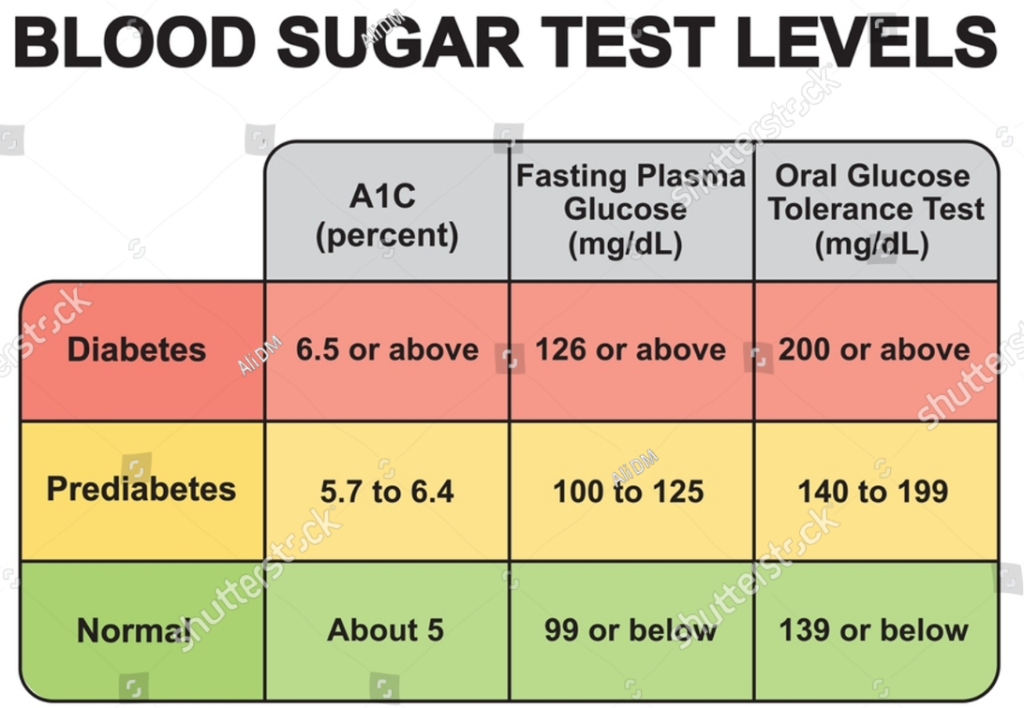
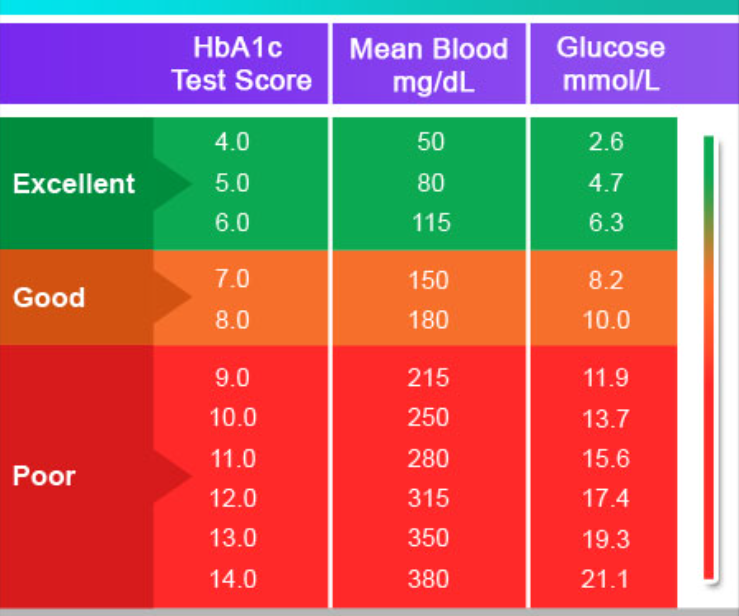
What is A1C or HbA1c test?
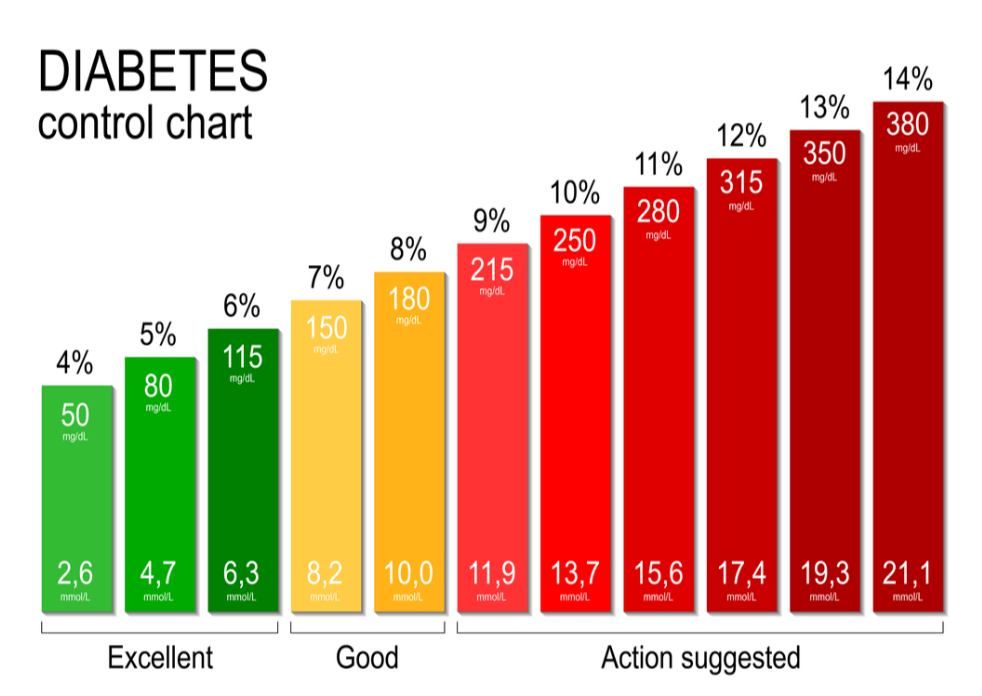
The A1C test, also known as the hemoglobin A1C or HbA1c test, is a blood test that measures your average blood sugar levels over the past 2-3 months. It’s a crucial tool for:
- Diagnosing prediabetes and type 2 diabetes: Higher A1C levels indicate poorer blood sugar control and increased risk of these conditions.
- Monitoring diabetes management: For people with diabetes, A1C helps track how well their treatment plan is working in controlling blood sugar levels.
Here’s how it works:
- Hemoglobin: A protein in red blood cells that carries oxygen.
- Glucose: A type of sugar that enters your bloodstream from food and fuels your body.
- Glycation: When glucose attaches to hemoglobin, it forms glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c).
What is Fasting Plasma Glucose?
Fasting plasma glucose (FPG) is a blood test that measures the level of glucose (sugar) in your blood after you haven’t eaten or drank anything (except water) for at least 8 hours, typically overnight. It’s a simple and common way to screen for prediabetes and diabetes, and to monitor blood sugar control in people with these conditions.
Fasting Plasma Glucose (FPG) is a blood test used to measure the levels of glucose (sugar) in your blood after a period of fasting. It’s commonly used to diagnose and monitor diabetes. Here’s how it works:
- Fasting Requirement: Before taking the test, you’re required to fast for at least 8 hours. This means no eating or drinking anything except water during this period. This fasting requirement is crucial because it ensures that food intake does not affect the blood sugar levels measured by the test.
- Blood Sample Collection: During the test, a blood sample is taken, usually from a vein in your arm.
- Glucose Measurement: The collected blood sample is then analyzed to measure the concentration of glucose in your plasma, which is the liquid part of your blood.
- Interpreting Results:
- Normal Range: Fasting plasma glucose levels are typically in the range of 70 to 99 milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL) for non-diabetics.
- Prediabetes Range: Levels between 100 mg/dL and 125 mg/dL are generally considered to indicate prediabetes.
- Diabetes Range: A fasting plasma glucose level of 126 mg/dL or higher on two separate tests is usually diagnostic for diabetes.
The FPG test is valuable because it’s a straightforward and reliable method for assessing blood sugar levels and the body’s ability to regulate glucose. It’s often part of routine health check-ups and is critical in managing diabetes and assessing the risk of developing this condition.
What is Oral glucose tolerance test?
The oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT) is a diagnostic procedure used to assess how well your body processes sugar (glucose). It’s primarily employed for:
- Diagnosing prediabetes and type 2 diabetes: If your body struggles to clear glucose from your bloodstream effectively, it can indicate prediabetes or diabetes.
- Monitoring gestational diabetes: This type of diabetes develops during pregnancy, and the OGTT helps assess blood sugar control in pregnant women.
Here’s how the OGTT works:
- Fasting: You’ll need to fast for at least 8 hours, typically overnight, before the test.
- Glucose drink: You’ll then drink a sugary solution containing a specific amount of glucose, usually 75g in 237ml of water.
- Blood draws: Blood samples will be taken at specific intervals, often at 0, 30, 60, 120, and 180 minutes after consuming the glucose drink.