What is Ingrown Hair?
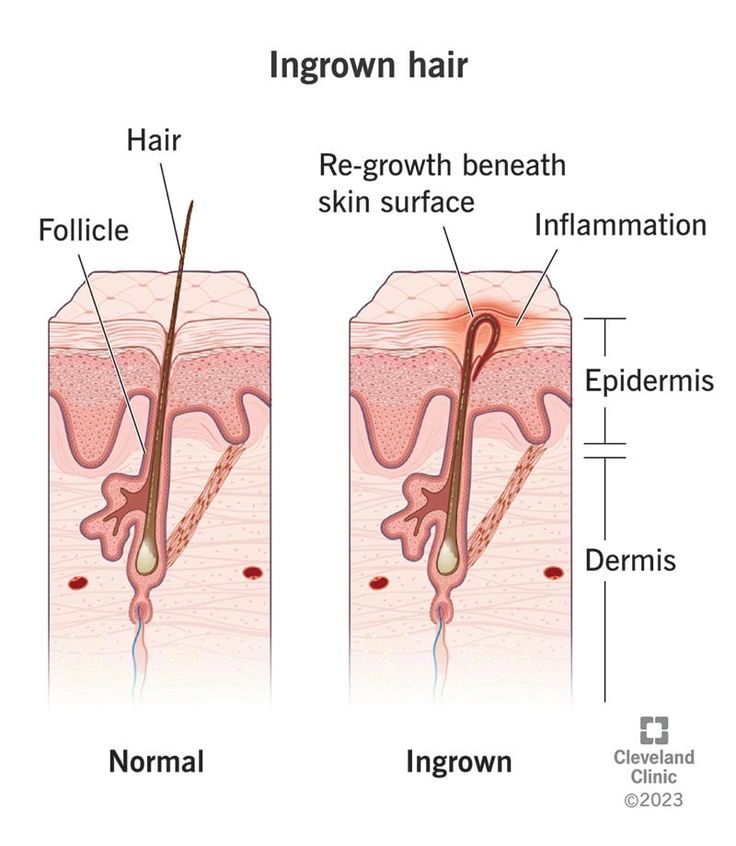
Ingrown hairs occur when hair grows back into the skin instead of up to the surface, often after shaving, tweezing, or waxing. They commonly affect individuals with curly hair, particularly Black people who shave. Symptoms include swollen, red, itchy, and sometimes painful bumps, hyperpigmentation, and pus-filled pimples. Tight clothing can contribute to ingrown hairs by causing friction. The immune system treats ingrown hairs as foreign objects, leading to inflammation and itching. Treatment involves stopping shaving, removing the hair follicle, or using topical medication. Ingrown hairs are more likely to develop if you have dry skin, shave close to the skin, use a blunt razor, or use hair removal products with irritating chemicals. This condition is common among people with coarse or curly hair, especially Black and Asian men on the face and neck and many women in the pubic area.
What are the Symptoms of Ingrown Hair?
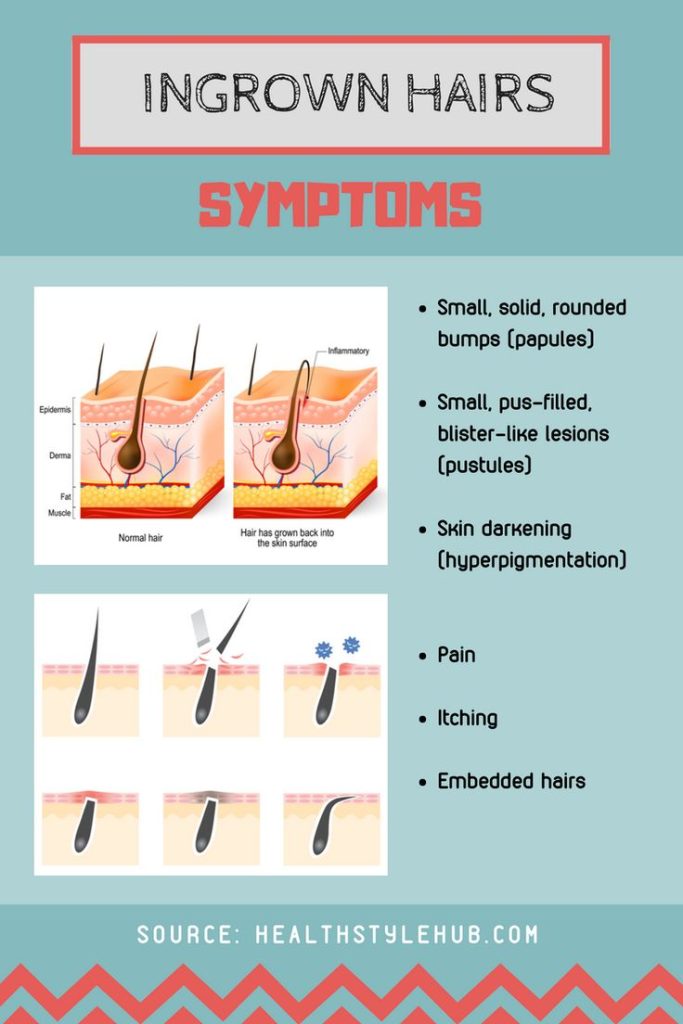
Symptoms of ingrown hairs can vary but commonly include:
- Tiny, swollen bumps where hair removal occurred (shaving, tweezing, or waxing).
- Small bumps resembling blisters or containing pus.
- Darker bumps compared to surrounding skin (hyperpigmentation).
- Sensations of burning or stinging.
- Itching.
- Hair with a looped shape due to the tip curving and growing into the skin.
Additional symptoms may include:
- Skin irritation.
- Small bumps with hairs in the center of the face and neck (papules).
- Pain.
- Discoloration of the affected area (red, brown, or purple).
- If the ingrown hair becomes infected, symptoms may worsen, including:
- Enlargement and increased pain of the bumps.
- Presence of pustules (pus-filled bumps).
- Increased redness around the ingrown hair.
- Swelling, appearing puffy or raised.
- Tenderness.
- Increased itching or irritation.
If you experience any of these symptoms, especially signs of infection, it’s important to seek medical attention to prevent potential complications.
How can I prevent Ingrown Hair?
To lower the chances of developing ingrown hairs, you can take several preventive measures:
- Avoid friction: Wear loose-fitting clothing to reduce irritation from friction on shaved areas.
- Choose the right products: Avoid solid antiperspirants that can block pores, opting for non-solid alternatives if you frequently experience underarm ingrown hairs.
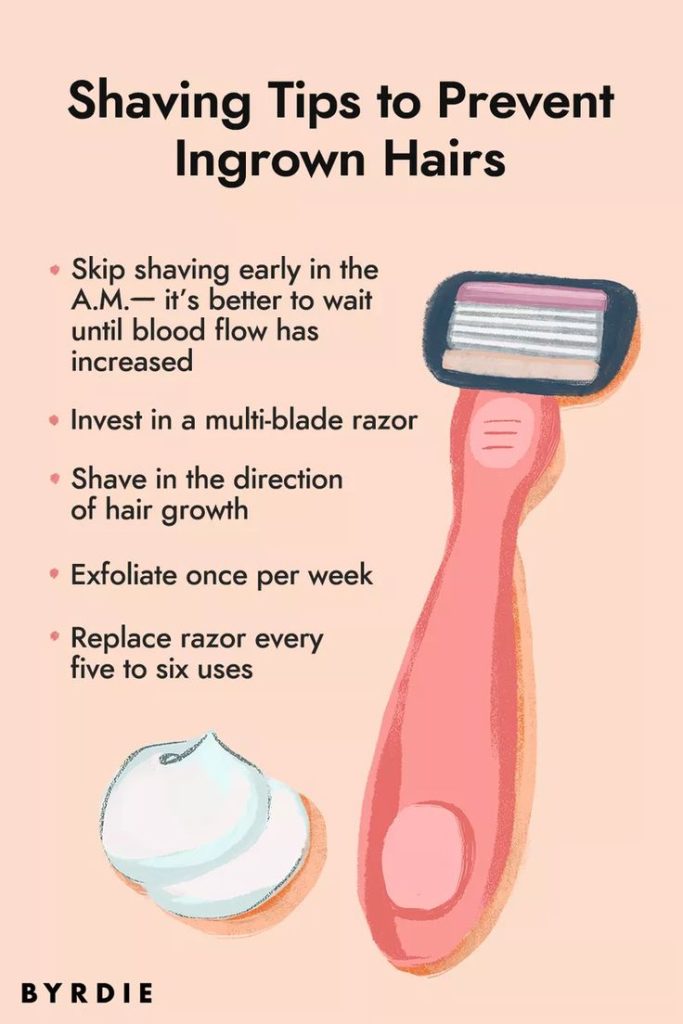
- Shave correctly: Glide the razor gently over your skin without pulling it taut, and use a special razor designed for sensitive skin, like a “bump fighter.” Shave or wax in the direction of hair growth.
- Maintain cleanliness: Shower after sweating, especially if you recently shaved or waxed, to prevent ingrown hairs from developing.
- Adjust hair length: Opt for longer hairstyles to prevent ingrown hairs on the scalp, and trim hair with scissors rather than clippers to avoid close shaves.
- Lubricate: Apply shave gel or cream to moisten the skin before shaving to help the razor glide smoothly, especially if you have sensitive skin.
- Use sharp razors: Replace razors regularly to ensure a sharp blade, reducing the risk of ingrown hairs and skin irritation.
- Other hair removal methods: Consider using electric razors or clippers instead of traditional razors, and test chemical hair removal products on a small patch of skin first to avoid irritation.
If you develop ingrown hair, avoid picking at it, allow it to breathe by wearing loose clothing, keep the area clean and moisturized, and avoid shaving or tweezing in the affected area to prevent further irritation and scarring. Specialized gels or serums may help the ingrown hair emerge, and if infection occurs, maintain cleanliness and seek medical attention if necessary.
What are the Complications of ingrown hairs?
- Bacterial Infection: Scratching can introduce bacteria, leading to infections.
- Postinflammatory Hyperpigmentation: Dark patches of skin due to the skin’s healing response.
- Keloids: Raised scars darker than surrounding skin.
- Pseudofolliculitis Barbae: Razor bumps caused by ingrown hairs.
- Fine Depressed Scars (Grooves): Scarring of the skin.
- Swelling, Redness, Itchiness, Pain: Symptoms around the ingrown hair.
- Pustules: Pus-filled bumps that can lead to secondary infections if popped.
- Secondary Skin Infections: Resulting from breaks in the skin from primary infections.
- Pus-filled Cysts or Nodules: Formed by forcing pus into deeper tissues.
- Scarring: Resulting from repeated or untreated ingrown hairs.
- Alteration of Skin’s Texture and Appearance: Changes in the skin’s appearance due to ingrown hairs.
- Keloid Formation: Raised, thickened scars extending beyond the original site.
How Can I Prevent Ingrown Hair?
- Pre-Shaving Preparations:
- Wash your skin with warm water and a mild facial cleanser before shaving.
- Apply lubricating shaving cream or gel to soften the hair.
- Use a sharp, single-blade razor, and avoid pulling your skin while shaving.
- Shave in the direction of hair growth to avoid too-close shaves.
- Rinse the blade after each stroke and apply a cool, wet cloth to the skin afterward.
- Post-Shaving Care:
- Apply a soothing after-shave product or glycolic acid lotion to help remove dead skin cells and prevent irritation.
- Avoid tight clothing that might rub against the ingrown hair.
- Keep the area clean and moisturized, using warm compresses to soften the skin if needed.
- Avoiding Ingrown Hairs:
- Don’t dig or pick at ingrown hairs.
- Avoid shaving or removing hair in the affected area to reduce irritation and scarring.
- Consider using formulated gels or serums to help the ingrown hairs come out more easily.
- General Tips for Hair Removal:
- Wash the skin before hair removal to prevent bacteria from entering.
- Change razors frequently and use shave gel and warm water during shaving.
- Use an exfoliating scrub to remove dead skin cells and prevent ingrown hairs.
- Shave or wax in the direction of hair growth and moisturize afterward.
- Consider alternative hair removal methods like laser treatment if ingrown hairs persist.
- Additional Preventive Measures:
- Avoid friction by wearing looser-fitting clothing in shaved areas.
- Use non-solid antiperspirants to prevent blocked pores.
- Shave gently without pulling the skin taut and use sharp razors.
- Shower after sweating, and consider leaving hair longer or switching hairstyles to prevent ingrown hairs.
- Apply shave gel or cream and use a fresh, sharp blade every time you shave.
- Avoid pulling or stretching the skin during shaving and moisturize regularly.
What are the Treatments of Ingrown Hair?

- Let it Heal:
- Allow the ingrown hair wound to heal completely before focusing on scar removal.
- Keep the area clean, covered, and moist to aid in the healing process.
- Sunscreen:
- Apply sunscreen to protect the scar from the sun and reduce discoloration.
- Green Tea:
- Use green tea extract topically, as it contains antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties that may aid in scar reduction.
- Aloe Vera:
- Apply fresh aloe vera gel directly from the plant onto the scar daily to promote healing.
- Onion Extract Gel:
- Products containing onion extract have shown effectiveness in reducing scar appearance, including keloid scars.
- Silicone:
- Silicone sheets or gels can be applied to scars to help reduce their appearance.
- Essential Oils:
- Diluted essential oils such as geranium, tea tree, and lavender may have healing properties that can aid in scar reduction.
- Over-the-counter Products:
- Consider using over-the-counter ingrown hair products, such as serums, lotions, toners, or pads containing gentle exfoliants.
- Warm Compresses:
- Apply warm, moist washcloths to the scarred area several times a day to help ease inflammation and promote drainage.
- Tweezing:
- If the ingrown hair is visible, carefully tweeze it out after cleaning the area with warm, soapy water.
- Gentle Exfoliation:
- Use gentle exfoliation techniques to help release trapped hairs, but be cautious as it may cause inflammation.
- Other Treatment Options:
- Consider topical treatments like topical tretinoin, topical antibiotics, steroid facial creams, glycolic acid lotion, or benzoyl peroxide.
- Prescription medications or procedures like laser hair removal or electrolysis may also be effective.