
Introduction & Background
In today’s world, social media has become an integral part of daily life, serving as a platform for communication, entertainment, and information. While social media can connect people globally, its excessive or unhealthy use can negatively impact mental health. As people curate their online lives, often showcasing only the best moments, users can develop unrealistic comparisons, leading to stress, anxiety, and other mental health challenges. The relationship between social media and mental health is a topic of growing concern as more individuals, especially teens and young adults, find their emotional well-being tied to their digital presence.
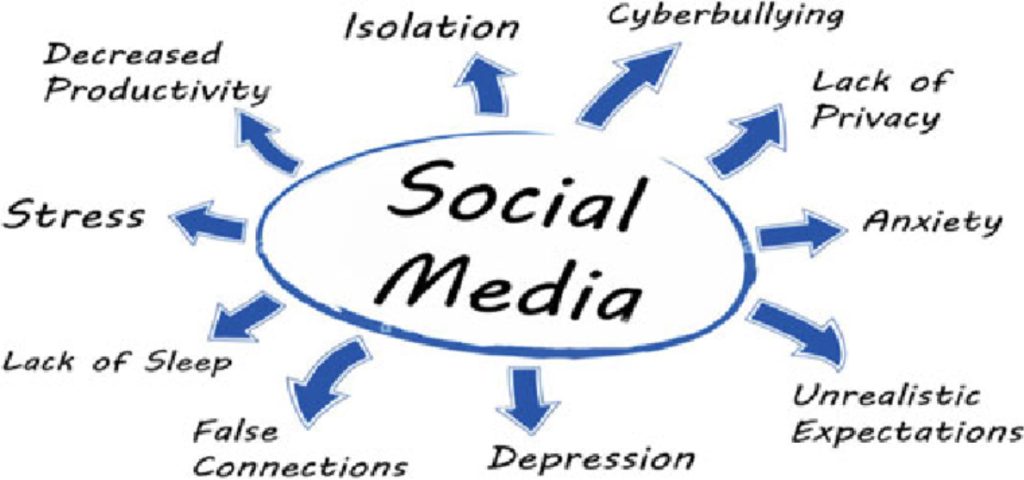
Causes of Social Media’s Impact on Mental Health
- Comparison Culture: Social media often showcases curated highlights of users’ lives, leading to feelings of inadequacy or envy when compared to one’s own experiences.
- Cyberbullying: The anonymity of social media can foster bullying, harassment, and negative interactions, which are emotionally damaging.
- Addiction: Many platforms are designed to be addictive, with features like infinite scrolling, which keep users engaged for extended periods and can increase anxiety.
- Fear of Missing Out (FOMO): Constant exposure to the experiences of others can create anxiety about missing out on events, opportunities, or social interactions.
- Unrealistic Expectations: The portrayal of perfection on platforms like Instagram can foster unhealthy standards related to body image, success, and lifestyle, which can lead to self-esteem issues and depression.
Indications of Social Media’s Impact on Mental Health
The following signs may indicate that social media is negatively affecting someone’s mental health:
- Obsession with Validation: Constantly checking for likes, comments, or followers for validation can signal social media dependence.
- Anxiety When Disconnected: Feeling anxious or irritable when unable to check social media indicates addiction.
- Avoidance of Real-Life Social Interactions: People may increasingly prefer online interactions, leading to social isolation.
- Mood Swings: Users may feel elated when receiving positive feedback but discouraged when engagement is low.
- Preoccupation with Social Media: Spending an excessive amount of time thinking about social media, planning posts, or analyzing interactions can disrupt daily life.
Symptoms of Social Media’s Impact on Mental Health
Social media’s impact can manifest in both psychological and physical symptoms:
- Anxiety: Regular use can increase stress, particularly if interactions are negative or induce feelings of comparison.
- Depression: Excessive use can lead to feelings of loneliness, inadequacy, and sadness.
- Sleep Disturbances: Late-night scrolling can disrupt sleep patterns and lead to insomnia, which exacerbates mental health issues.
- Low Self-Esteem: Regular comparisons with others online can erode self-worth, especially among young users.
- Isolation: Despite being highly connected online, users may feel disconnected from meaningful, real-world interactions.

Prevention Strategies for Social Media’s Impact on Mental Health
- Set Time Limits: Regulate daily social media usage by setting screen time limits to avoid overuse.
- Curate Content: Follow accounts that promote positivity and mute or unfollow accounts that cause negative emotions.
- Practice Digital Detox: Regularly take breaks from social media to focus on offline activities.
- Engage in Real-Life Activities: Prioritize face-to-face interactions with family and friends over digital ones.
- Mindfulness: Practice mindfulness and stress-relieving techniques such as meditation to improve mental resilience against social media-related stress.
Myths and Facts About Social Media’s Impact on Mental Health
- Myth: Social media only affects teens and young adults.
- Fact: People of all ages can experience negative mental health impacts from excessive social media use.
- Myth: Social media is inherently bad for mental health.
- Fact: When used mindfully, social media can foster positive connections and provide support, but overuse can lead to negative outcomes.
- Myth: Only direct interactions like cyberbullying impact mental health.
- Fact: Passive consumption of content, like scrolling through feeds, can also have subtle negative effects by promoting comparison and isolation.
Treatments and Therapy for Social Media-Related Mental Health Issues
1. Medication-Based Treatments
- Antidepressants and anti-anxiety medications can be prescribed in cases where social media usage exacerbates or triggers depression and anxiety disorders.
2. Surgical Treatments
- Not applicable: Surgical intervention is not used for treating mental health issues caused by social media.
3. Physical Therapy and Rehabilitation
- Exercise Programs: Physical activity, yoga, or rehabilitation exercises can help reduce the mental strain caused by social media addiction by releasing endorphins and reducing stress.
4. Lifestyle and Behavioral Interventions
- Behavioral Changes: Setting boundaries for social media use and adopting healthier habits, such as spending time outdoors or engaging in offline hobbies, can positively affect mental health.
5. Alternative and Complementary Medicine
- Meditation and Mindfulness: Practices like meditation, deep breathing exercises, and mindfulness can help mitigate anxiety and stress triggered by social media.
6. Psychotherapy and Counseling
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): Often used to address negative thought patterns related to social media. It can help users reframe how they perceive their online interactions.
- Talk Therapy: Provides a safe space for individuals to discuss their struggles with social media and its impact on their mental health.
7. Immunizations and Vaccines
- Not applicable: There are no vaccines for mental health issues caused by social media usage.
8. Stem Cell Therapy
- Not applicable: Stem cell therapy is not a treatment for social media-induced mental health problems.
9. Gene Therapy
- Not applicable: Gene therapy does not apply to the treatment of mental health conditions related to social media use.
Top 20 FAQ on Social Media’s Impact on Mental Health
- How does social media affect mental health?
- Social media can lead to anxiety, depression, low self-esteem, and social isolation, especially with excessive use.
- Can social media cause depression?
- Yes, the constant comparison, negative interactions, and feelings of inadequacy triggered by social media can contribute to depression.
- Why do people feel anxious about their social media presence?
- Users often seek validation through likes, comments, and engagement, which can lead to anxiety about their social media posts.
- Can quitting social media improve mental health?
- Yes, studies show that reducing or quitting social media can improve mood, reduce anxiety, and enhance overall well-being.
- What are signs of social media addiction?
- Obsession with checking social media, anxiety when not using it, and neglect of real-world relationships and activities.
- Can social media affect sleep?
- Yes, late-night scrolling and exposure to screens can disrupt sleep patterns, leading to insomnia and poor sleep quality.
- What age group is most affected by social media’s mental health effects?
- Teens and young adults are more susceptible, though all age groups can be impacted.
- Can social media lead to eating disorders?
- Social media can contribute to body image issues, potentially leading to disordered eating behaviors.
- How does social media cause FOMO?
- Seeing others enjoy experiences in real-time can make users feel left out, leading to anxiety and dissatisfaction.
- How can parents help manage their children’s social media use?
- By setting screen time limits, monitoring usage, and encouraging offline activities.
- Can social media exacerbate social anxiety?
- Yes, constant interaction and pressure to perform online can worsen social anxiety.
- What are positive uses of social media for mental health?
- Support groups, mental health awareness, and connecting with loved ones.
- Can cyberbullying on social media lead to mental health issues?
- Yes, cyberbullying can cause severe emotional distress, anxiety, and depression.
- Is social media bad for everyone?
- No, when used mindfully, it can foster connections and support. The impact depends on how it is used.
- Can excessive use of social media lead to real-world social isolation?
- Yes, over-reliance on online interactions can reduce face-to-face communication.
- How can mindfulness help with social media-related stress?
- Mindfulness practices can help users manage stress, remain grounded, and reduce anxiety from social media use.
- Are there apps to help limit social media usage?
- Yes, apps like Freedom and Screen Time help limit social media usage and promote healthier habits.
- What should I do if social media is making me feel anxious?
- Consider limiting your usage, curating a positive feed, or seeking professional help.
- Does social media impact body image?
- Yes, exposure to idealized body standards can negatively affect body image, especially in young adults.
- Can therapy help manage social media addiction?
- Yes, therapy, especially CBT, can help individuals address underlying issues related to social media dependence.

Conclusion
Social media is a powerful tool, but like any tool, its impact on mental health depends on how it’s used. By being mindful of the causes, symptoms, and preventive strategies, individuals can better manage their relationship with social media. For those experiencing significant mental health challenges as arelationship, therapy and interventions such as CBT can significantly help individuals manage the emotional impact of social media use. By promoting awareness and adopting preventive strategies, it’s possible to enjoy the benefits of social media while minimizing its negative effects on mental health. Prioritizing real-world connections and taking regular digital breaks are crucial steps toward healthier social media habits.