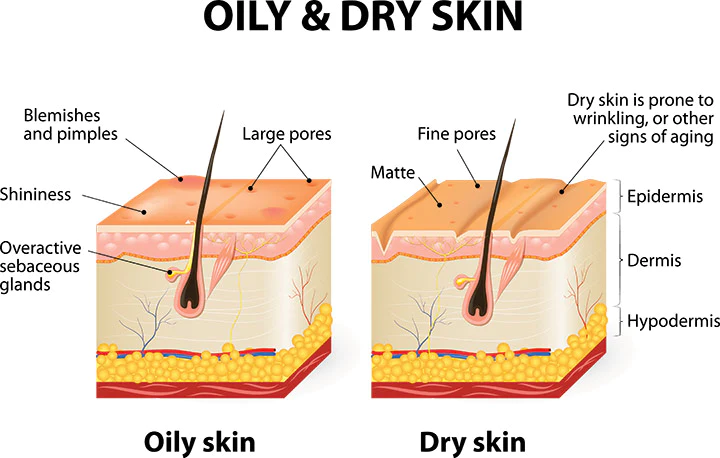
The prevalence of oily skin is a widespread dermatological concern, affecting individuals regardless of acne presence and contributing to concerns about enlarged pores and a perceived “unclean” or “greasy” appearance. The market response is evident, with thousands of products targeting oily skin available on platforms like Amazon, ranging widely in price and claiming various benefits. Some high-end products even blend modern technology with traditional healing ingredients to address oily or acne-prone skin. Despite the demand for effective treatments, the underlying reasons for variations in sebum production leading to oily skin remain elusive, making it challenging to identify a universally successful treatment. Several factors have been proposed as contributors to oily skin, adding to the complexity of finding a single effective solution. In this context, the review delves into the physiology of sebaceous glands and explores both current and emerging treatment options for individuals seeking relief from oily skin concerns. Notably, the review focuses on discussing individual active ingredients rather than providing evaluations of specific over-the-counter products, citing a lack of objective data in that regard.
Treatments for oily skin:-
1. Gentle Cleansing: (i)Use a Mild Cleanser:
- Opt for a gentle, fragrance-free cleanser designed for oily or acne-prone skin. Look for key terms like “non-comedogenic” and “oil-free” on the product labels.
- Gel-based or foaming cleansers are often suitable for oily skin, as they help remove excess oil and impurities without stripping the skin.
(ii)Frequency of Cleansing: Cleanse your face twice a day, in the morning and before bedtime. Over-cleansing can stimulate more oil production, so striking a balance is essential.
(iii)Avoid Harsh Ingredients: Steer clear of harsh ingredients like alcohol, as they can be overly drying and may prompt the skin to produce more oil to compensate.
(iv)Salicylic Acid or Benzoyl Peroxide: Consider using a cleanser with salicylic acid or benzoyl peroxide as these ingredients can help control oil production and prevent breakouts. However, start with a lower concentration to prevent potential irritation.
(v)Warm Water Rinse: Use lukewarm water to rinse your face. Hot water can strip the skin of its natural oils, leading to increased oil production.
(vi)Pat, Don’t Rub: Gently pat your face dry with a clean towel instead of rubbing vigorously. This helps avoid irritation and ensures some natural oils remain on the skin.
(vii)Non-comedogenic Moisturizer: Even oily skin needs hydration. Choose a non-comedogenic, oil-free moisturizer to keep the skin balanced. This can help prevent the skin from producing excess oil to compensate for dryness.
(viii)Exfoliation: Include a mild exfoliant in your routine, such as a chemical exfoliant with ingredients like alpha hydroxy acids (AHAs) or beta hydroxy acids (BHAs). This can help remove dead skin cells and prevent clogged pores.
(ix)Patch Test: Introduce new products gradually and perform patch tests to ensure your skin doesn’t react negatively to any specific ingredient.
2. Exfoliation: Exfoliation involves removing dead skin cells from the skin’s outer layer, promoting a lighter, brighter, and more youthful appearance. This can be achieved through the use of grainy substances, exfoliating tools, or chemical agents. While the skin naturally sheds these cells, exfoliation accelerates the process for enhanced results. However, improper exfoliation based on your skin type can lead to irritation, damage, or breakouts. Before starting an exfoliation routine, it’s crucial to:
- Know Your Skin Type:
- Understand whether your skin is normal, oily, dry, sensitive, or a combination. Different skin types may require specific exfoliation approaches.
- Consider Current Skincare Products:
- Take into account the beauty and skincare products you already use. Some medications or treatments, such as those containing retinol or benzoyl peroxide, can increase skin sensitivity.
- Precautions with Medications:
- Be cautious if using medications or treatments that may heighten skin sensitivity. Combining these with exfoliation could worsen dryness or trigger breakouts.
(i)Choose the Right Exfoliant:Opt for chemical exfoliants containing ingredients like salicylic acid (BHA), glycolic acid (AHA), or lactic acid. These ingredients penetrate the skin to break down and remove dead skin cells, excess oil, and other impurities.
(ii)Start Slow: If you’re new to exfoliation, start with a lower concentration of the exfoliating agent. This allows your skin to adjust and minimizes the risk of irritation.
(iii)Frequency of Exfoliation: Oily skin can generally tolerate more frequent exfoliation, but it’s important not to overdo it. Start with exfoliating once or twice a week and adjust based on how your skin responds.
(iv)Avoid Physical Scrubs: Steer clear of abrasive physical scrubs with rough particles, as they can irritate the skin and potentially worsen oiliness. Chemical exfoliants are usually gentler and more effective for oily skin.
(v)Use Salicylic Acid for Deeper Penetration: Salicylic acid is particularly beneficial for oily skin as it is oil-soluble and can penetrate deep into the pores, helping to dissolve excess oil and prevent acne breakouts.
(vi)Consider Combination Exfoliants: Some products contain a combination of AHAs and BHAs, providing a more comprehensive exfoliation. However, these may be more suitable for individuals who have built up tolerance to individual acids.
(vii)Sun Protection is Essential: Exfoliation can make your skin more sensitive to sunlight. Always use a broad-spectrum sunscreen with at least SPF 30 during the day, even on cloudy days, to protect your skin from UV damage.
(viii)Moisturize Adequately: Exfoliation can sometimes lead to temporary dryness. Ensure you use a non-comedogenic moisturizer to keep your skin hydrated without causing further oiliness.
(ix)Skip Exfoliation if Irritated: If your skin becomes irritated, red, or overly sensitive, skip exfoliation until your skin has calmed down. Over-exfoliation can compromise the skin barrier and worsen oiliness.
(x)Consult a Dermatologist: If you have concerns about your skincare routine or experience persistent issues with oily skin, consulting with a dermatologist can help determine the most suitable exfoliation routine for your specific needs.
3. Oil-Free Moisturizers:
The popularity of oil-free moisturizers prompts the question of their significance, especially considering that oils play a crucial role in skin hydration. Oil-free moisturizers are particularly advantageous for individuals with oily skin. This skin type is inherently abundant in natural hydration, and an oil-free moisturizer is designed to provide a light, balanced level of hydration without exacerbating oiliness. For those with oily skin, the skin’s natural oils already fulfill the role of additional oils, making heavy occlusive moisturizers less necessary. The primary theoretical advantage of oil-free moisturizers lies in their potential to be non-comedogenic, meaning they are less likely to clog pores and contribute to acne. Therefore, when choosing a moisturizer, the key consideration, especially for individuals prone to acne, is whether it is non-comedogenic. This ensures that the moisturizer won’t contribute to the formation of comedones (clogged pores), supporting healthier and clearer skin. Ultimately, the choice between oil-free and traditional moisturizers depends on individual skin needs, with oil-free options being particularly suitable for those with oily skin seeking balanced hydration without additional oiliness.
4. Use a Clay Mask: Clay masks can help absorb excess oil and unclog pores. Look for masks containing ingredients like kaolin or bentonite clay. Various types of clays are popular in skincare, each offering unique benefits.
Types of Clay Mask:-(i)Bentonite Clay:
- Properties: Highly potent and known for its strong detoxifying abilities. It effectively draws out impurities from the skin’s surface and can counter bacterial infections.
- Consideration: Best suited for those with less sensitive skin, as it may be drying.
(ii)Rhassoul Clay:
- Properties: An ancient, mineral-rich clay with powerful detoxifying properties. Acts as a magnet for toxins, sebum, blackheads, and bacteria.
- Consideration: Gentle and less likely to dry out the skin compared to Bentonite.
(iii)Kaolin Clay:
- Properties: A gentle clay suitable for sensitive skin. White Kaolin clay is ideal for mild exfoliation but lacks the intense detoxification properties of Bentonite.
- Consideration: Comes in different varieties, such as yellow, pink, or red, with deeper hues having a higher ability to absorb toxins.
(iv)Green Clay:
- Properties: Commonly used for skincare, it absorbs oils and impurities while promoting blood circulation, giving a tingling sensation.
- Consideration: The green color indicates quality; it should not appear grey or white.

5. Oil-Free Sunscreen: Despite common misconceptions, individuals with oily skin should not skip sunscreen. Sunscreen is a crucial component of skincare, offering protection against harmful UV rays and contributing to healthy-looking skin. Regular sunscreen use provides anti-aging benefits, reduces the risk of sunspots, and helps prevent skin cancer. For those with oily skin, it’s important to find a suitable oil-free sunscreen that balances sun protection without exacerbating oiliness. Look for formulas designed for oily skin, often featuring lightweight, non-greasy, and quick-absorbing properties. Ingredients such as zinc oxide, titanium dioxide, avobenzone, or octocrylene are commonly found in oil-free sunscreens. Consistent application, even on cloudy days, is key for effective sun protection and long-term skin health.
(i)Look for “Oil-Free” or “Non-Comedogenic” Labels: Opt for sunscreens specifically labeled as “oil-free” or “non-comedogenic.” These formulations are designed to provide sun protection without clogging pores or adding excess oil to the skin.
(ii)Choose a Gel-Based or Water-Based Formula: Gel-based or water-based sunscreens tend to be lighter and absorb quickly, making them suitable for oily skin. These formulations often provide a matte finish, reducing the appearance of shine.
(iii)Check for Broad-Spectrum Protection: Ensure that the sunscreen offers broad-spectrum protection, covering both UVA and UVB rays. Look for SPF 30 or higher for effective sun protection.
(iv)Consider Mattifying Ingredients: Some oil-free sunscreens include mattifying ingredients, such as silica or powders, to help control excess oil and shine throughout the day.
(v)Avoid Heavy Creams: Steer clear of heavy, creamy sunscreens, as they may feel too thick on oily skin and contribute to a greasy appearance.
(vi)Apply the Right Amount: Use the recommended amount of sunscreen for your face and neck. Applying too much can lead to a heavier feel on the skin.
(vii)Reapply Throughout the Day: Reapply the sunscreen every two hours, or more frequently if you’re sweating or swimming. This is essential for maintaining adequate sun protection.
(viii)Try Tinted Formulas: Tinted sunscreens can offer additional benefits by providing some coverage for blemishes and reducing the need for additional makeup.
(ix)Perform Patch Tests: If you have sensitive skin or are trying a new sunscreen, perform a patch test to ensure it doesn’t cause irritation or breakouts.
(x)Double Cleansing at Night: Since sunscreen can be more resilient, especially water-resistant formulations, consider using an oil-free cleanser or micellar water for effective removal at the end of the day.
6. Topical Retinoids: Retinoids, such as retinol or prescription-strength tretinoin, can help regulate oil production and promote cell turnover. Start with lower concentrations to avoid irritation.Topical retinoids are a class of skincare ingredients derived from vitamin A that are known for their effectiveness in addressing various skin concerns, including oily skin.

(i)Regulation of Sebum Production: Topical retinoids, such as tretinoin, adapalene, and tazarotene, have been shown to regulate sebum (oil) production. They help normalize the function of the sebaceous glands, reducing excessive oiliness.
(ii)Unclogging Pores: Retinoids work by promoting cell turnover and preventing the formation of comedones (clogged pores). By keeping pores clear, they help prevent the development of acne and reduce the appearance of blackheads and whiteheads.
(iii)Anti-Inflammatory Properties: Retinoids possess anti-inflammatory properties, making them effective in managing inflammatory acne lesions. They can help reduce redness and swelling associated with acne breakouts.
(iv)Improvement of Skin Texture: Regular use of topical retinoids can contribute to the improvement of skin texture. They promote collagen production and enhance skin renewal, leading to smoother and more even-toned skin.
(v)Treatment of Acne: Topical retinoids are commonly prescribed for acne treatment, making them beneficial for individuals with oily, acne-prone skin. They target various factors contributing to acne development.
(vi)Prevention of Photodamage: Retinoids have photoprotective effects, helping to prevent and repair damage caused by exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation. This is especially important as individuals with oily skin may be prone to photodamage.
(vii)Choosing the Right Formulation: Individuals with oily skin may benefit from gel-based or lightweight formulations of retinoids, as these are less likely to contribute to a greasy or heavy feel on the skin.
(viii)Gradual Introduction: It’s advisable to introduce retinoids gradually to allow the skin to acclimate. Starting with a lower concentration and applying the product a few times a week can help minimize potential irritation.
(ix)Consistent Sunscreen Use: Since retinoids can increase skin sensitivity to sunlight, it’s crucial to use sunscreen daily. This is important for overall skin health and to prevent potential sun damage.
7. Salicylic Acid: Salicylic acid is a beta-hydroxy acid (BHA) that is widely used in skincare, particularly for individuals with oily or acne-prone skin.

(i)Exfoliation and Unclogging Pores: Salicylic acid is known for its exfoliating properties. It penetrates oil-filled pores and exfoliates the dead skin cells, helping to unclog pores and prevent the formation of acne lesions.
(ii)Oil Control: Salicylic acid helps control excess oil production by regulating sebum (skin oil) levels. This is particularly beneficial for individuals with oily skin who are prone to shine and enlarged pores.
(iii)Acne Treatment: Salicylic acid is effective in treating various types of acne, including blackheads, whiteheads, and inflammatory acne lesions. It has anti-inflammatory properties that can help reduce redness and swelling
(iv) Improvement of Skin Texture: Regular use of salicylic acid can contribute to the improvement of skin texture. It promotes cell turnover, leading to smoother and more even-toned skin.
(v)Prevention of Breakouts: By keeping pores clear and reducing excess oil, salicylic acid helps prevent new acne breakouts. It is often included in skincare products designed for acne prevention.
(vi)Suitable for Oily and Combination Skin: Salicylic acid is well-suited for individuals with oily or combination skin types. It is oil-soluble, allowing it to penetrate through oil and effectively target acne-prone areas.
(vii)Consideration for Sensitivity: While salicylic acid is generally well-tolerated, individuals with sensitive skin may experience some dryness or irritation. It’s advisable to start with a lower concentration and gradually increase frequency to allow the skin to adjust.
(viii)Incorporating Into Skincare Routine: Salicylic acid can be found in various skincare products, including cleansers, toners, spot treatments, and serums. It’s important to choose the right formulation and concentration based on your skin’s needs.
(ix)Consistent Sunscreen Use: Since salicylic acid may increase skin sensitivity to sunlight, it’s crucial to use sunscreen daily, especially when using products containing this ingredient.
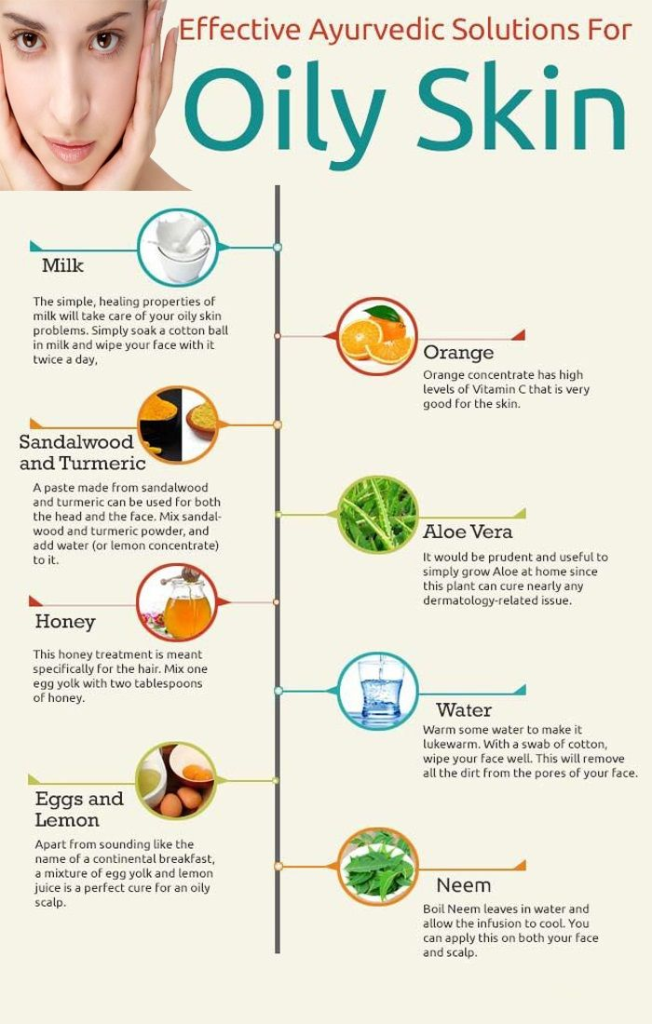
8. Hydration and Diet: Hydration and diet play essential roles in maintaining overall skin health, including managing oily skin.
Hydration:
(i)Drink Plenty of Water:Staying well-hydrated is important for overall skin health. Drinking an adequate amount of water helps flush out toxins from the body and can contribute to a more balanced complexion.
(ii)Use a Lightweight Moisturizer:Even oily skin needs hydration. Opt for oil-free or lightweight moisturizers to keep the skin hydrated without adding excess oil. Look for non-comedogenic formulations to avoid clogging pores.
(iii)Consider Hydrating Ingredients: Hydrating ingredients like hyaluronic acid can help attract and retain moisture in the skin. Look for products that contain these ingredients for effective hydration.
(iv)Humectants and Gel-Based Products: Products with humectants, such as glycerin, can draw moisture to the skin. Gel-based products are often suitable for oily skin, providing hydration without a heavy feel.
(v)Hydrating Masks: Consider using hydrating masks occasionally. Look for masks with ingredients like aloe vera or hyaluronic acid to provide an extra boost of hydration.
Diet:
(i)Balanced Diet: A balanced and nutrient-rich diet is crucial for overall skin health. Include a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats in your meals.
(ii)Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Omega-3 fatty acids, found in foods like fatty fish, flaxseeds, and walnuts, have anti-inflammatory properties that may benefit individuals with oily skin.
(iii)Limit Processed Foods and Sugars: Processed foods and those high in sugars can contribute to inflammation and may impact the overall health of your skin. Limiting these in your diet can have positive effects.
(iv)Antioxidant-Rich Foods: Include foods rich in antioxidants, such as berries, spinach, and green tea. Antioxidants help combat oxidative stress and support skin health.
(v)Vitamin A and Zinc: Foods rich in vitamin A (e.g., sweet potatoes, carrots) and zinc (e.g., nuts, seeds, legumes) can be beneficial for individuals with oily skin. These nutrients play a role in skin health and oil regulation.
(vi)Stay Hydrated Through Foods: Hydrate your body not only with water but also through water-rich foods like watermelon, cucumber, and celery.
9. Avoid Harsh Products: Avoiding harsh products is crucial for individuals with oily skin to maintain a healthy and balanced complexion.Avoid harsh astringents and products with high alcohol content, as they can strip the skin and potentially worsen oiliness.
(i)Avoid Over-Cleansing: Harsh fragrances can be irritating, especially for sensitive or oily skin. Opt for fragrance-free or products with light, non-irritating scents.
(ii)Say No to Alcohol-Based Products: Products containing high levels of alcohol can be overly drying and irritating for oily skin. Look for alcohol-free alternatives to prevent stripping the skin of essential moisture.
(iii)Gentle Exfoliation: While exfoliation is beneficial, harsh exfoliants or abrasive scrubs can cause microtears in the skin, leading to irritation and increased oiliness. Choose gentle exfoliants, preferably chemical exfoliants like salicylic acid, and use them in moderation.
(iv)Avoid Products with Harsh Fragrances: Harsh fragrances can be irritating, especially for sensitive or oily skin. Opt for fragrance-free or products with light, non-irritating scents.
(v)Beware of High pH Cleansers:Cleansers with high pH levels can disrupt the skin’s natural acid mantle, leading to imbalances and increased oil production. Choose cleansers with a balanced pH, typically around 5.5.
(vi)Be Cautious with Strong Acids:While some acids like salicylic acid can be beneficial for oily skin, strong concentrations or frequent use can lead to irritation. Start with lower concentrations and gradually increase if needed.
(vii)Non-Comedogenic Products:Look for products labeled as non-comedogenic. These products are formulated to avoid clogging pores, preventing the formation of blackheads and acne.
(viii)Avoid Heavy, Oil-Based Moisturizers:Opt for oil-free or non-comedogenic moisturizers to avoid adding unnecessary oil to the skin. Gel-based or water-based formulations are often suitable for oily skin.
(ix)Patch Test New Products:Before incorporating new products into your routine, perform a patch test to ensure they don’t cause irritation or breakouts.
(x)Consult with a Dermatologist:If you’re unsure about which products are suitable for your oily skin, consult with a dermatologist. They can provide personalized recommendations based on your specific skin needs.
10. Blotting Papers:Keep blotting papers on hand to absorb excess oil throughout the day without disturbing your makeup.Blotting papers are a popular and effective solution for managing excess oil on the skin, especially for individuals with oily skin.
(i)Quick Oil Absorption: Blotting papers are designed to quickly absorb excess oil on the skin’s surface, helping to reduce shine without disturbing makeup.
(ii)Portable and Convenient: Compact and easy to carry, blotting papers are convenient for on-the-go use. They can be discreetly used throughout the day to control oiliness without the need for additional products.
(iii)Preserves Makeup: Instead of applying more powder to combat shine, blotting papers offer a solution to remove oil while preserving your makeup.
(iv)Minimizes Breakouts: By removing excess oil, blotting papers can help minimize the risk of clogged pores and reduce the likelihood of breakouts associated with oily skin.
(v)Variety of Types: Blotting papers come in various types, including traditional paper-based sheets and those made from natural materials like rice or hemp. Choose a type that suits your preferences and skin needs.
11.Prescription Medications:Prescription medications for oily skin are typically recommended when over-the-counter products and lifestyle changes are insufficient in managing excess oil production.
(i)Topical Retinoids:
- Examples: Tretinoin, Adapalene, Tazarotene
- How They Work: Topical retinoids are derivatives of vitamin A that promote cell turnover, unclog pores, and regulate oil production. They are commonly prescribed for acne but can also help with oily skin.
(ii)Topical Antibiotics:
- Examples: Clindamycin, Erythromycin
- How They Work: Topical antibiotics can be prescribed to reduce acne-related inflammation and control the growth of acne-causing bacteria. They may help in managing both acne and oily skin.
(iii)Oral Antibiotics:
- Examples: Doxycycline, Minocycline, Tetracycline
- How They Work: Oral antibiotics are sometimes prescribed for more severe cases of acne and oily skin. They help reduce inflammation and control bacterial growth.
(iv)Oral Contraceptives (Birth Control Pills):
- Examples: Yaz, Ortho Tri-Cyclen
- How They Work: Hormonal birth control pills containing both estrogen and progestin can help regulate hormonal fluctuations that contribute to oily skin. They are often prescribed for females with hormonal acne.
(v)Isotretinoin (Accutane):Isotretinoin is a powerful oral retinoid used for severe acne that hasn’t responded to other treatments. It significantly reduces oil gland size and the amount of oil produced.
(vi)Spironolactone:Spironolactone is an anti-androgen medication that is sometimes prescribed off-label for women with hormonal acne and excess oil production. It helps reduce oiliness by blocking androgens (male hormones)
(vii)Glycolic Acid Peels:Chemical peels, often performed by dermatologists, involve the application of glycolic acid to the skin. They can help exfoliate the skin, control oil production, and improve overall skin texture.
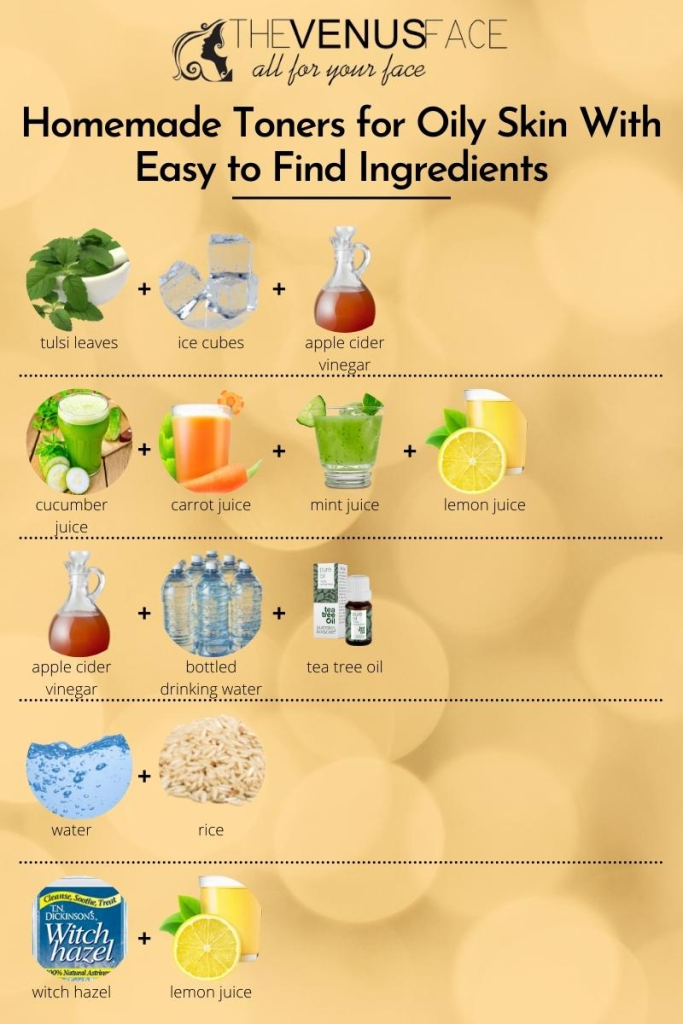
11.Facial Toners:Some toners containing gentle astringents like witch hazel or rose water can help balance oil production.Facial toners can be a beneficial addition to a skincare routine for individuals with oily skin.
(i)Alcohol-Free Formulas: Avoid toners with high alcohol content, as they can be overly drying and may stimulate the skin to produce more oil to compensate.
(ii)Non-Comedogenic Ingredients: Look for toners that are labeled as non-comedogenic. These products are formulated to avoid clogging pores, which is particularly important for individuals with oily skin prone to acne.
(iii)Hydrating Ingredients: Despite having oily skin, it’s essential to maintain skin hydration. Choose toners that contain hydrating ingredients such as glycerin or hyaluronic acid.
(iv)Mild Astringents: Some toners for oily skin contain mild astringents, such as witch hazel, which can help control oil and minimize pores. However, it’s crucial to avoid toners with harsh astringents that may cause irritation.
(v)Salicylic Acid: Salicylic acid is a beta-hydroxy acid (BHA) that is effective for oily and acne-prone skin. It helps exfoliate the skin, unclog pores, and control oil production. Look for toners with a lower concentration of salicylic acid for daily use.
(vi)Glycolic Acid: Glycolic acid is an alpha-hydroxy acid (AHA) that exfoliates the skin and helps improve its texture. It can be beneficial for oily skin but should be used in moderation.
(vii)Niacinamide (Vitamin B3): Niacinamide has anti-inflammatory properties and helps regulate sebum production. Toners with niacinamide can be suitable for individuals with oily skin.
(viii)Matte Finish: Look for toners that leave a matte finish on the skin. These formulations can help reduce shine and provide a smooth canvas for the rest of your skincare or makeup routine.
(ix)Tea Tree Oil: Tea tree oil has antimicrobial properties and can be beneficial for controlling oil and preventing breakouts. However, it’s important to use it in diluted form to avoid skin irritation.
(x)pH-Balanced Formulas: Toners with a pH-balanced formula are gentler on the skin and help maintain the skin’s natural barrier. Look for toners with a pH close to the skin’s natural pH, which is around 4.7 to 5.75.