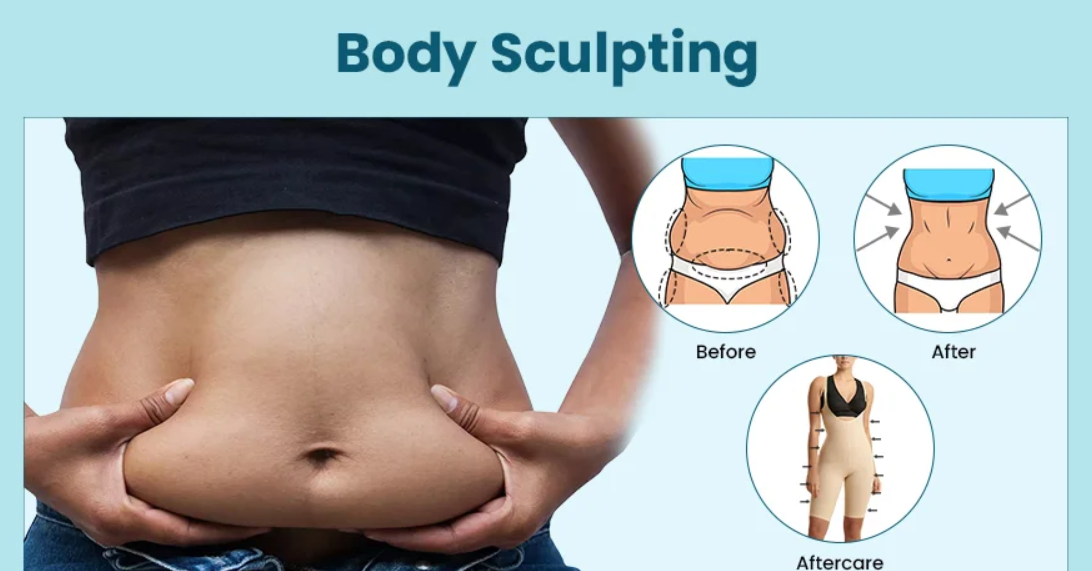
Introduction to Body Sculpting
Spinal fusion is a surgical procedure designed to join two or more vertebrae in the spine, eliminating motion between them. It is commonly performed to treat conditions that cause spinal instability or severe back pain, such as degenerative disc disease, spondylolisthesis, spinal fractures, herniated discs, or certain types of spinal deformities. The goal of spinal fusion is to stabilize the spine, alleviate pain, and restore functionality by fusing the vertebrae into a single, solid unit.
During the procedure, the surgeon typically removes the damaged disc between the vertebrae and replaces it with a bone graft. The graft may come from the patient's own bone (autograft), from a donor (allograft), or from synthetic materials. In some cases, metal plates, screws, or rods are also used to hold the vertebrae in place while the fusion process takes place. Over time, the bone graft grows and fuses the vertebrae together, creating a stable spinal segment.
Spinal fusion is usually done under general anesthesia, and the procedure can be approached from the front (anterior), back (posterior), or side (lateral) of the spine, depending on the location of the problem. It can be performed as an open surgery or through a minimally invasive technique, which involves smaller incisions and potentially faster recovery times.
After surgery, recovery typically involves a period of immobilization, followed by physical therapy to strengthen the back and improve flexibility. While spinal fusion can significantly improve pain and stability, it does have risks, such as infection, nerve damage, or complications related to the implanted hardware.
In summary, spinal fusion is a highly effective surgical option for individuals with debilitating spinal conditions that cause chronic pain and instability, offering long-term relief and better quality of life for many patients. However, it requires careful consideration of the risks, benefits, and recovery process.
Causes and Risks of Body Sculpting
Body sculpting is a popular cosmetic procedure designed to shape and contour the body, often through methods like liposuction, non-invasive fat reduction, or even surgical procedures such as tummy tucks. While it can significantly enhance one's appearance, it also comes with potential causes for undergoing the procedure and certain risks to be aware of. Let's break down the causes and risks involved in body sculpting.
Causes for Seeking Body Sculpting
Body sculpting is generally pursued when individuals have areas of fat, skin, or muscle that have proven difficult to address with conventional methods like dieting and exercise. Some of the most common reasons people seek body sculpting include:
-
Stubborn Fat: Certain areas of fat, such as love handles, abdomen, thighs, or chin, often don't respond to diet or exercise. Body sculpting helps target and reduce this fat, leading to a more toned appearance.
-
Post-Weight Loss: After significant weight loss, loose skin or fat deposits can persist in various parts of the body. Body sculpting helps eliminate excess skin or fat, providing a more contoured look.
-
Aging: As we age, skin elasticity decreases, leading to sagging or looser skin in areas such as the abdomen, thighs, or arms. Body sculpting procedures can tighten the skin and reduce the appearance of wrinkles or sagging.
-
Genetics: Some individuals may be genetically predisposed to store fat in specific areas, such as the thighs, abdomen, or chin. Body sculpting helps reduce these localized fat deposits, offering a more balanced body shape.
Risks of Body Sculpting Procedures
While body sculpting procedures can be incredibly effective, there are potential risks and complications involved, especially when dealing with surgical procedures. Some of the risks include:
-
Scarring: Surgical body sculpting methods such as liposuction or tummy tucks can leave permanent scarring, though surgeons do their best to place incisions in discreet areas.
-
Infection: As with any surgical procedure, there is a risk of infection. Maintaining proper hygiene and following post-surgical care instructions are vital for minimizing this risk.
-
Uneven Results: In some cases, the results may not be as smooth or even as expected. This can happen if fat removal is not done evenly, or if skin tightening is not consistent.
-
Seroma or Hematoma: Fluid or blood collection under the skin can occur post-surgery, requiring drainage.
-
Anesthesia Risks: With any procedure involving anesthesia, there are potential risks of allergic reactions or complications.
-
Pain and Swelling: Following non-surgical body sculpting treatments, there may be some pain, swelling, and bruising, which is typically temporary.
-
Emotional Considerations: The psychological impact of body sculpting procedures, such as unrealistic expectations or dissatisfaction with the results, can lead to emotional distress.
Symptoms and Signs That May Benefit from Body Sculpting
Body sculpting is most beneficial for individuals who are seeking to reshape their bodies and improve areas of stubborn fat or excess skin that are resistant to diet and exercise. Some common symptoms or signs that indicate you may benefit from body sculpting include:
1. Excess Fat in Targeted Areas
-
Localized fat deposits in the abdomen, thighs, hips, back, chin, or arms that won't diminish with exercise or dietary changes.
-
Areas of fat bulges that create an unbalanced silhouette or that make it difficult to wear certain clothes.
2. Loose or Sagging Skin
-
After significant weight loss, you may notice loose, sagging skin, particularly around the abdomen, flanks, upper arms, or thighs.
-
Stretch marks or skin that has lost elasticity following pregnancy, aging, or weight loss.
3. Lack of Muscle Definition
-
Areas where muscle tone could be more defined (like the abdomen or arms) but have stubborn fat deposits or excess skin hiding muscle definition.
4. Psychological Distress
-
Dissatisfaction with body appearance after weight loss, pregnancy, or aging, leading to decreased self-esteem or body dysmorphia.
Diagnosis of Body Sculpting
The first step toward body sculpting is an initial consultation with a qualified surgeon or aesthetic professional. During this consultation, the provider will assess several factors to determine the most appropriate treatment. The diagnosis process typically involves:
1. Medical History Evaluation
A thorough evaluation of the patient's medical history will be conducted, including any previous surgeries, underlying health conditions (such as diabetes or heart disease), and lifestyle habits (e.g., smoking or alcohol use).
2. Physical Examination
The surgeon will examine the areas of concern, assessing skin elasticity, fat deposits, muscle tone, and the overall health of the treated areas. The goal is to understand the extent of excess fat, skin laxity, or uneven body contouring.
3. Discussing Goals and Expectations
The surgeon or consultant will discuss the patient's aesthetic goals to ensure the desired results align with the procedures available. For example, do you want to focus on fat removal, skin tightening, or muscle definition?
4. Personalized Treatment Plan
Based on the evaluation, the provider will recommend the most suitable procedure, which may include liposuction, coolsculpting, radiofrequency treatments, or non-invasive skin tightening procedures.
Treatment Options for Body Sculpting
Body sculpting is a cosmetic procedure aimed at reshaping and contouring the body to achieve a more toned and aesthetically pleasing appearance. The treatment options can broadly be divided into non-invasive, minimally invasive, and surgical methods, depending on the desired results, area of treatment, and recovery time. Each option has its unique benefits, limitations, and suitability for different individuals.
1. Surgical Body Sculpting
Liposuction
One of the most popular body sculpting procedures, liposuction is a surgical procedure that removes fat through a small tube inserted into the body. It can treat various areas like the abdomen, flanks, hips, and thighs, and helps patients achieve a contoured appearance.
-
Ideal for: Individuals with localized fat resistant to diet and exercise.
-
Procedure: Performed under general anesthesia, a surgeon makes small incisions, through which fat is suctioned out.
-
Recovery: There may be bruising, swelling, and discomfort, but most people return to regular activities within 1-2 weeks.
Tummy Tuck (Abdominoplasty)
This procedure removes excess skin and fat from the abdomen while tightening the abdominal muscles. It is commonly performed after significant weight loss or pregnancy.
-
Ideal for: Individuals with excess abdominal skin or weak abdominal muscles.
-
Procedure: The surgeon makes an incision along the lower abdomen, removes excess skin, and tightens the abdominal muscles.
-
Recovery: It can take several weeks for full recovery, with restrictions on heavy lifting and activity during the healing period.
2. Non-Surgical Body Sculpting
CoolSculpting
CoolSculpting is a non-invasive procedure that freezes fat cells, causing them to break down naturally over time.
-
Ideal for: Individuals with small pockets of fat that do not respond to exercise or diet.
-
Procedure: A special applicator is placed on the target area, and cooling is applied to the skin.
-
Recovery: Minimal downtime, with some mild swelling or bruising post-treatment. Results are visible in several weeks.
Ultrasound Therapy (Ultherapy)
Ultherapy uses focused ultrasound waves to stimulate collagen production and tighten skin without surgery.
-
Ideal for: Individuals with mild to moderate skin laxity who want to avoid surgery.
-
Procedure: The practitioner uses an ultrasound device to target deep layers of the skin.
-
Recovery: No downtime, though patients may experience mild redness or swelling post-treatment.
Radiofrequency (RF) Treatments
RF devices use heat to stimulate collagen production and tighten skin.
-
Ideal for: Individuals with mild sagging or skin laxity in areas like the abdomen, thighs, or neck.
-
Procedure: Non-invasive; heat energy is applied to the skin to stimulate collagen.
-
Recovery: Quick with minimal downtime.
Prevention and Management of Body Sculpting
Once you've undergone a body sculpting procedure, maintaining your results is crucial for long-term satisfaction. Here are some prevention and management strategies:
1. Maintain a Stable Weight
Since body sculpting doesn't prevent future weight gain, it is important to maintain a healthy weight through balanced nutrition and regular exercise.
2. Healthy Diet and Exercise
Adopting a lifestyle that includes regular physical activity (including strength training and cardiovascular exercises) and a balanced diet will help preserve your body sculpting results.
3. Regular Skin Care
Moisturizing and protecting your skin can improve its elasticity and prevent sagging. Consider using firming creams and products with collagen-stimulating ingredients.
Complications of Body Sculpting
As with any cosmetic procedure, there are risks involved with body sculpting. Some common complications include:
-
Scarring: Surgical procedures like liposuction and tummy tucks can leave permanent scars.
-
Uneven Results: Some areas may experience irregular contours or lumps after fat removal.
-
Infection: Any procedure that breaks the skin's surface carries the risk of infection.
-
Swelling and Bruising: Post-procedure swelling and bruising are common and can last for a few weeks.
Living with the Condition and Body Sculpting
Living with the condition of body sculpting involves both physical and psychological aspects. Body sculpting, often associated with procedures like liposuction or non-invasive treatments, aims to alter the shape and contour of the body. While many people seek body sculpting for cosmetic reasons, living with the results or the ongoing pursuit of body sculpting requires careful consideration of both its benefits and challenges.
1. Post-Treatment Care
-
After treatment, it is important to follow all post-surgery or post-procedure instructions carefully to ensure optimal results.
-
Compression garments may be required for a few weeks after liposuction or tummy tucks to help reduce swelling and promote skin tightening.
2. Psychological Benefits
-
Many patients report a significant boost in self-esteem and confidence after body sculpting, which translates into improved quality of life and greater social engagement.
3. Long-Term Maintenance
Maintaining the results of body sculpting requires a long-term commitment to healthy living, including exercise, a balanced diet, and consistent self-care.
Top 10 Frequently Asked Questions about Body Sculpting
1. What is body sculpting?
Body sculpting, also known as body contouring, is a cosmetic procedure designed to shape and improve the appearance of the body. It can involve surgical or non-surgical methods that target areas of fat, skin, and muscle to create a more toned, sculpted appearance. Common body sculpting procedures include liposuction, CoolSculpting, laser body contouring, and tummy tucks.
2. What areas of the body can be treated with body sculpting?
Body sculpting can target various areas of the body where excess fat, skin, or muscle issues are present. Common treatment areas include:
-
Abdomen
-
Thighs (inner, outer, or saddlebags)
-
Flanks (love handles)
-
Buttocks
-
Arms (bat wings)
-
Chin (double chin)
-
Back (bra bulge)
Different techniques may be used depending on the area being treated and the desired outcome.
3. What are the different types of body sculpting procedures?
There are both surgical and non-surgical body sculpting options:
-
Surgical Body Sculpting: Includes procedures like liposuction, tummy tuck (abdominoplasty), facelifts, and body lifts. These procedures are invasive, typically require anesthesia, and involve recovery time.
-
Non-surgical Body Sculpting: Includes methods such as CoolSculpting (cryolipolysis), laser lipolysis, radiofrequency treatments, ultrasound fat reduction, and Kybella (for chin fat). These options are less invasive, typically require no downtime, and are designed to reduce fat and contour the body.
4. How does non-surgical body sculpting work?
Non-surgical body sculpting works by using energy-based technologies to target and break down fat cells. Common techniques include:
-
CoolSculpting: Uses cold temperatures to freeze and destroy fat cells, which are then naturally eliminated by the body.
-
Laser lipolysis: Uses laser energy to melt fat under the skin, which is then absorbed by the body.
-
Radiofrequency and ultrasound: Use heat or sound waves to break down fat and tighten skin.
These treatments are generally non-invasive, require little to no downtime, and have minimal risk of complications.
5. How long does it take to see results from body sculpting?
The timeline for results varies depending on the procedure:
-
Surgical body sculpting (e.g., liposuction) typically shows results within 6-8 weeks, with final results visible after 3-6 months as swelling continues to subside.
-
Non-surgical procedures like CoolSculpting may take 3-4 weeks to start seeing visible results, with the final effects becoming noticeable after 2-3 months as fat is gradually eliminated.
Multiple sessions may be required for optimal results, depending on the treatment.
6. What is the recovery time for body sculpting?
Recovery time depends on the type of procedure:
-
Surgical body sculpting: Recovery times vary based on the procedure. For example, liposuction requires 1-2 weeks for initial recovery, with swelling and bruising subsiding over the next few weeks. Full recovery may take 3-6 months.
-
Non-surgical body sculpting: Procedures like CoolSculpting typically require no downtime, with some patients returning to normal activities immediately. Mild redness, swelling, or soreness may occur for a few days.
7. Are the results of body sculpting permanent?
The results of body sculpting can be long-lasting but are not necessarily permanent.
-
Surgical procedures like liposuction or tummy tucks provide lasting results, but weight gain or lifestyle changes can affect the results.
-
Non-surgical body sculpting results can last as long as the fat cells are eliminated, but if the patient gains weight, new fat cells can develop in other areas. Maintaining a stable weight and healthy lifestyle is key to preserving the results.
8. How much does body sculpting cost?
The cost of body sculpting varies depending on the procedure, the treatment area, and the clinic's location. On average:
-
Non-surgical body sculpting can range from $1,500 to $4,000 per session for treatments like CoolSculpting.
-
Surgical body sculpting procedures, such as liposuction, may cost anywhere from $2,500 to $7,000 or more, depending on the extent of the treatment.
Consulting with a board-certified plastic surgeon or licensed practitioner can provide a more accurate estimate based on your specific needs.
9. Who is a good candidate for body sculpting?
A good candidate for body sculpting is someone who:
-
Has stubborn pockets of fat or areas of the body that are resistant to diet and exercise
-
Is in good overall health and close to their ideal weight
-
Has realistic expectations and understands that body sculpting is not a weight-loss procedure
-
Is seeking improvement in body contour rather than dramatic changes
A consultation with a qualified professional can determine if you're a suitable candidate for the procedure.
10. Are there any risks or side effects associated with body sculpting?
Like any cosmetic procedure, body sculpting carries some risks:
-
Surgical body sculpting can lead to complications such as infection, bleeding, scarring, or seroma (fluid buildup).
-
Non-surgical body sculpting may result in temporary redness, swelling, numbness, or bruising. These side effects typically resolve on their own within a few days to weeks.
It's important to choose a qualified practitioner and follow all post-treatment care instructions to minimize risks and achieve the best results.


