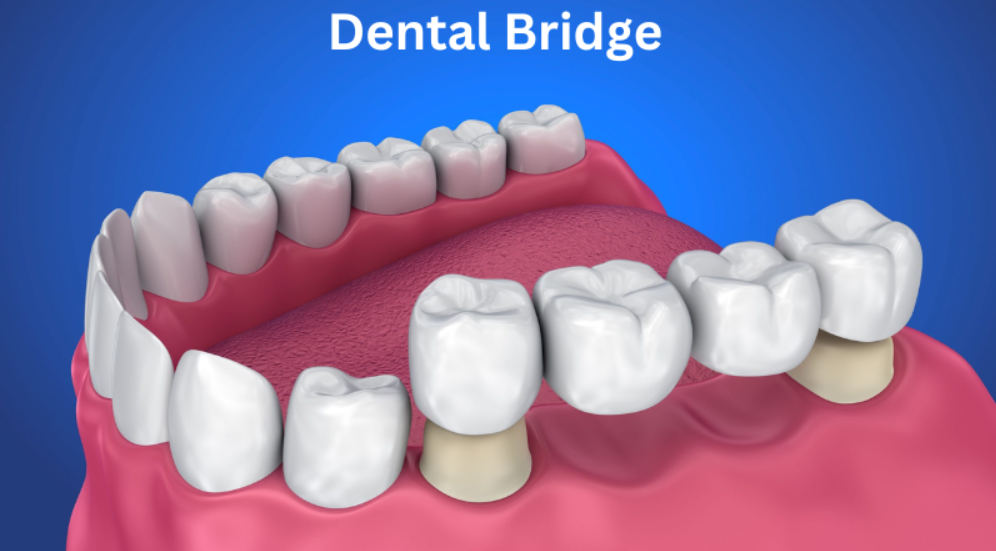
Introduction to Dental Bridges
Dental bridges are one of the most popular and effective solutions for replacing missing teeth. They are a type of fixed dental restoration that fills the gap left by one or more missing teeth. As the name suggests, dental bridges “bridge” the space between two healthy teeth or dental implants, offering both functional and aesthetic benefits. These restorations are designed to restore the normal function of chewing and speaking, which can be significantly affected when a tooth or teeth are lost.
The bridge itself consists of several components, including a false tooth, known as the pontic, and the surrounding abutment teeth that support the pontic. The pontic is typically made from a variety of durable materials such as porcelain, ceramic, or metal, and it's custom-designed to match the color, shape, and size of the natural teeth. The abutment teeth, which are the teeth adjacent to the missing one, are either natural teeth that are prepared by a dentist to fit crowns or dental implants. These crowns or implants serve as the foundation that holds the bridge in place.
Dental bridges are essential not only for restoring appearance but also for improving oral health. Missing teeth can lead to a variety of dental issues, including shifting of remaining teeth, difficulty chewing, and speaking problems. Moreover, missing teeth can place unnecessary strain on the jawbone, leading to bone loss over time. A dental bridge, in addition to providing aesthetic benefits, helps prevent these issues by maintaining the alignment of the teeth and restoring the normal bite.
Causes and Risk Factors for Needing a Dental Bridge
There are many reasons why you may lose a tooth or multiple teeth, and each of these can result in the need for a dental bridge. Understanding the causes and risk factors that contribute to tooth loss can help you better manage your oral health and potentially avoid the need for restorative treatments like dental bridges.
1. Tooth Decay
Tooth decay is one of the most common causes of tooth loss. Over time, plaque and bacteria build up on the teeth, eroding the tooth enamel and leading to cavities. If the decay progresses to the point where the tooth is no longer structurally sound, extraction becomes necessary. Dental bridges are an ideal solution to replace the lost tooth and restore function. The pontic (false tooth) used in the bridge fills the space left by the decayed tooth, and the surrounding teeth are prepared to serve as support.
2. Gum Disease (Periodontitis)
Gum disease, especially when it progresses to its advanced stage, periodontitis, can significantly damage the teeth and gums. Periodontitis affects the tissues and bones that hold the teeth in place, often leading to tooth mobility and even tooth loss. This can happen when the gums become inflamed due to plaque buildup that isn't properly managed. Once a tooth is lost due to gum disease, a dental bridge can restore the smile and prevent further complications.
3. Trauma or Injury
Trauma to the mouth from accidents or injuries can result in broken or lost teeth. When a tooth is knocked out, fractured, or severely damaged, a dental bridge is often the most suitable restoration option. Bridges restore the natural appearance of the smile while also improving the functionality of the mouth, enabling the patient to chew and speak properly again.
4. Congenital Absence
Some individuals are born without certain teeth, a condition known as hypodontia or congenital absence. This can be particularly noticeable when the missing teeth are in highly visible areas such as the front of the mouth. In these cases, dental bridges offer an effective way to restore both appearance and function.
5. Wear and Tear
As we age, the wear and tear on our teeth can cause significant damage, leading to tooth loss. Additionally, habits such as teeth grinding (bruxism) can exacerbate this problem, causing the enamel to break down and teeth to weaken. In some cases, extensive wear may necessitate the use of a dental bridge to restore the function and appearance of the smile.
6. Risk Factors for Tooth Loss
Certain lifestyle factors and health conditions can increase the risk of tooth loss. Smoking, for instance, is linked to an increased risk of gum disease and poor healing after dental procedures. Diabetes can also impact gum health and wound healing, making individuals with diabetes more susceptible to tooth loss. Maintaining a balanced diet, practicing good oral hygiene, and visiting the dentist regularly can help prevent these conditions from leading to tooth loss.
Symptoms and Signs Indicating the Need for a Dental Bridge
When you lose a tooth, the effects can be both functional and aesthetic. Missing teeth can impact how you speak, chew, and smile. Here are some common symptoms and signs that suggest the need for a dental bridge:
1. Visible Gaps Between Teeth
The most obvious sign that you may need a dental bridge is the visible gap left by a missing tooth. A missing tooth, particularly in the front, can have a significant impact on your smile and appearance. For those who are self-conscious about the gap, a dental bridge provides a solution that restores the smile and overall confidence.
2. Shifting of Adjacent Teeth
When a tooth is lost, the surrounding teeth often begin to shift into the empty space. This can lead to bite problems, misalignment, and crooked teeth. A dental bridge helps keep the adjacent teeth in place by preventing them from shifting, helping to maintain a natural bite.
3. Difficulty Chewing or Speaking
Losing a tooth can make chewing difficult, particularly if the missing tooth is in the back of the mouth. Without the proper support, chewing food properly becomes a challenge. A dental bridge restores the functionality of your teeth, making it easier to chew and enjoy a variety of foods. Similarly, missing teeth can cause speech issues, particularly with pronunciation. A bridge helps restore normal speech patterns.
4. Self-Consciousness About Smile
Many individuals feel embarrassed or self-conscious when they are missing teeth, especially if the missing teeth are in a visible area. This can lead to avoidance of social situations and lack of confidence. Dental bridges provide a natural-looking restoration that helps restore the appearance of your smile and allows you to feel confident again.
Diagnosis of Dental Bridge Necessity
Before recommending a dental bridge, a dentist will thoroughly assess your oral health. Several diagnostic steps are taken to ensure that a dental bridge is the most appropriate solution for you.
1. Clinical Examination
The dentist will begin by performing a complete examination of your oral cavity, which includes checking for missing or damaged teeth, as well as assessing the overall health of your gums and remaining teeth. This initial evaluation helps the dentist determine the best treatment approach.
2. X-rays and Imaging
To get a deeper understanding of your oral health, the dentist will take X-rays of your mouth. These images allow the dentist to evaluate the bone structure, the condition of the surrounding teeth, and any signs of infection or decay. X-rays also help determine whether there is enough healthy bone to support a dental implant if necessary.
3. Dental Impressions
After a thorough examination and imaging, the dentist will take impressions of your teeth to create a model of your mouth. These impressions are essential for designing a custom dental bridge that will fit comfortably and match the color, shape, and alignment of your existing teeth.
4. Medical History Review
Your dentist will also ask about your medical history, including any conditions that could affect the healing process or impact your treatment. For example, diabetes may slow healing, or certain medications may affect your oral health. This information will guide the dentist in choosing the right treatment plan for you.
Treatment Options for Dental Bridges
There are different types of dental bridges, and the right choice depends on your individual situation. The following are the most common types of bridges used today:
1. Traditional Bridges
Traditional bridges are the most widely used type of dental bridge. They consist of a false tooth (pontic) that is held in place by crowns placed on the adjacent natural teeth. The abutment teeth are prepared by trimming them to fit the crowns. This method is ideal for individuals who have strong, healthy adjacent teeth that can support the bridge.
2. Cantilever Bridges
Cantilever bridges are used when only one adjacent tooth is available to support the bridge. These bridges are anchored on one side and extend into the gap, offering a solution when only one tooth is present to support the bridge. This type of bridge is often used for replacing teeth located in less visible areas.
3. Maryland Bridges
Maryland bridges, also known as resin-bonded bridges, are a less invasive option. They use a metal or porcelain framework that is bonded to the back of the adjacent teeth instead of using crowns. This method is ideal for replacing front teeth and requires less preparation of the adjacent teeth.
4. Implant-Supported Bridges
Implant-supported bridges are used when the patient does not have healthy teeth to support a traditional bridge. These bridges are supported by dental implants, which are placed directly into the jawbone. This option is more stable and durable than traditional bridges and is ideal for patients with sufficient bone structure.
Prevention and Management of Dental Bridges
Once a dental bridge is in place, it's crucial to care for it properly to ensure its longevity. With good oral hygiene and regular dental checkups, your bridge can last for many years.
1. Maintain Good Oral Hygiene
Brushing and flossing are essential for preventing plaque buildup and gum disease around your bridge. Use a soft-bristled toothbrush to clean your teeth, gums, and bridge. Flossing should be done with a floss threader to clean under the bridge and between the abutments.
2. Regular Dental Checkups
Regular dental checkups are essential to ensure the health of your bridge and the surrounding teeth. Your dentist will inspect the bridge, check for any signs of damage or decay, and make sure the surrounding gums are healthy.
3. Avoid Hard or Sticky Foods
Hard foods like nuts and sticky foods like caramel can damage or dislodge your bridge. Avoid these foods to prolong the life of your bridge.
4. Use a Mouthguard if Necessary
If you grind your teeth at night, using a mouthguard can protect both your natural teeth and your dental bridge from unnecessary wear and tear.
Complications Associated with Dental Bridges
While dental bridges are effective and long-lasting, they can encounter issues. Some potential complications include:
1. Tooth Decay
If the adjacent teeth are not adequately cleaned, they may develop cavities or other issues that can affect the stability of the bridge.
2. Gum Disease
Poor oral hygiene can lead to gum disease, which may cause inflammation around the bridge. Regular brushing and flossing can help prevent gum disease.
3. Bridge Failure
In rare cases, a dental bridge can fail due to excessive wear or damage. This is often due to poor oral hygiene, excessive pressure from teeth grinding, or the bridge becoming loose over time.
Living with a Dental Bridge
Getting used to a dental bridge requires some adjustment, but with time, most patients find that the bridge becomes a natural part of their oral routine.
1. Getting Used to the Feel
Initially, the bridge may feel slightly bulky or uncomfortable. However, after a few days, most patients adapt to the sensation, and the bridge should feel just like a natural tooth.
2. Dietary Adjustments
In the first few weeks, you may need to avoid certain foods that are hard or sticky. As you adjust to the bridge, you can slowly introduce a broader range of foods into your diet.
3. Long-Term Care
With proper care, your dental bridge can last for many years. Routine checkups, good oral hygiene, and avoiding damaging habits will help extend the life of your bridge.
Top 10 Frequently Asked Questions about Dental Bridges
1. What are dental bridges?
A dental bridge is a fixed (non-removable) dental restoration designed to replace one or more missing teeth. The bridge is anchored to the natural teeth (abutment teeth) on either side of the gap or can be supported by dental implants. The false tooth, often referred to as a pontic, fills the space where the tooth is missing, creating a more complete and functional smile. Bridges help restore the normal function of teeth, such as chewing and speaking, and also help maintain the shape of your face.
Why are they important?
Dental bridges are essential for restoring both the aesthetics and functionality of your
teeth. They prevent your remaining teeth from shifting into the empty space, which can
cause misalignment and lead to further dental issues.
2. How long do dental bridges last?
The lifespan of dental bridges can vary, typically lasting anywhere from 5 to 15 years, depending on various factors such as:
-
Material used: Bridges made from porcelain or ceramic tend to last longer compared to those made from less durable materials like resin.
-
Oral hygiene: Proper care, including brushing and flossing, can significantly extend the life of your bridge.
-
Diet and habits: Avoiding hard foods, biting on non-food objects, and not grinding teeth can help preserve the integrity of the bridge.
-
Maintenance and check-ups: Regular dental visits to check for signs of wear and tear will help maintain the longevity of your bridge.
In some cases, if a bridge is damaged or if the supporting teeth are weakened, it may need to be replaced before its expected lifespan is over.
3. What types of dental bridges are there?
There are several types of dental bridges, and your dentist will recommend the best one based on the location of the missing tooth, the health of your remaining teeth, and other individual factors. The common types of dental bridges include:
-
Traditional Bridges: These are the most common type and are typically used when there are natural teeth on both sides of the gap. The false tooth is held in place by crowns that are cemented to the abutment teeth.
-
Cantilever Bridges: These are used when there is only one adjacent tooth to support the bridge. The pontic is attached to a crown on the one remaining tooth, making it a simpler, but less stable solution compared to a traditional bridge.
-
Maryland Bridges (Resin-bonded bridges): This type is typically used for missing front teeth. Instead of using crowns, the bridge is bonded to the adjacent teeth using a metal or porcelain framework with a false tooth in the middle. It's a more conservative option since it doesn't require much alteration to the supporting teeth.
-
Implant-supported Bridges: Instead of relying on natural teeth for support, this type uses dental implants. Multiple implants are placed in the jawbone, and the bridge is then anchored to them. This is a more permanent and secure option and is often recommended for people who have multiple missing teeth.
Each type of bridge has its benefits, and your dentist will help you choose the right one for your needs.
4. Are dental bridges covered by insurance?
In most cases, dental bridges are partially covered by dental insurance, especially if they are deemed medically necessary. However, coverage varies significantly depending on your insurance provider and plan. Some plans may cover a percentage of the procedure cost, while others may have a waiting period or limit coverage to certain types of bridges.
To determine exactly what's covered, contact your insurance provider and ask about the specifics of your dental plan, including the materials used for the bridge and the dentist you visit. Additionally, some dental plans may have exclusions related to cosmetic procedures, so it's important to clarify your insurance terms with your provider beforehand.
5. How do I take care of a dental bridge?
Proper care and maintenance are crucial to the longevity of your dental bridge. Here are some tips to ensure your bridge lasts as long as possible:
-
Brushing: Brush your teeth and bridge at least twice a day using a soft-bristled toothbrush. Be sure to clean around the bridge and under the pontic to avoid plaque build-up, which can lead to tooth decay or gum disease.
-
Flossing: Use special floss or a floss threader to clean between your bridge and the supporting teeth. Regular flossing will help remove food particles and plaque that may accumulate, especially around the crown areas.
-
Regular Dental Visits: It's essential to visit your dentist regularly for professional cleanings and check-ups. Your dentist will examine the bridge to ensure it fits correctly and hasn't become loose or damaged.
-
Avoid Hard or Sticky Foods: Hard foods, such as ice or sticky candies, can damage your bridge. It's a good idea to avoid biting into such foods, especially if your bridge is held together by natural teeth.
6. Can dental bridges be replaced?
Yes, dental bridges can be replaced if necessary. Over time, a bridge may wear down, or the supporting teeth may become weakened or damaged. If the bridge becomes loose or doesn't fit properly anymore, it will need to be replaced.
Additionally, if the bridge develops decay or the underlying gums show signs of infection, a new bridge might be required. If a bridge becomes severely damaged or uncomfortable, your dentist will discuss the best course of action for replacement, which may include considering dental implants for more stability.
7. What are the risks of getting a dental bridge?
Like any dental procedure, there are potential risks associated with getting a dental bridge. Some of the risks include:
-
Damage to adjacent teeth: The supporting teeth may need to be reduced in size to accommodate crowns, which could cause the teeth to become weak or more susceptible to cavities.
-
Gum disease: If the bridge isn't maintained properly, bacteria can accumulate around the bridge and cause gum disease, which could lead to tooth loss or other complications.
-
Discomfort or Sensitivity: After the bridge is placed, some patients experience discomfort or sensitivity, especially when consuming hot or cold foods and beverages. However, this should subside over time.
-
Bridge Failure: In some cases, a bridge may not bond correctly, leading to a need for adjustments or even a replacement.
8. How is the process of getting a dental bridge done?
The process of getting a dental bridge usually takes two to three visits to the dentist:
-
Visit 1: During the first visit, the dentist will prepare the supporting teeth by reducing them in size to make room for crowns. Impressions of your teeth will be taken to create a custom bridge that fits perfectly. A temporary bridge will be placed to protect the prepared teeth until the permanent bridge is ready.
-
Visit 2: Once the bridge is made, the dentist will remove the temporary bridge and place the permanent one. Adjustments will be made to ensure a comfortable fit. The bridge will then be permanently cemented in place.
9. Are there alternatives to dental bridges?
Yes, there are several alternatives to dental bridges, depending on the specific needs of the patient:
-
Dental Implants: Dental implants are a more permanent and durable solution for replacing missing teeth. An implant is surgically placed into the jawbone, serving as a foundation for a crown or bridge.
-
Partial Dentures: Partial dentures are removable prosthetic devices that can replace one or more missing teeth. They are often more affordable than bridges but may not be as secure or permanent.
-
Flipper Teeth: A flipper is a temporary removable partial denture that replaces missing teeth, but it is not a long-term solution.
Each option has its pros and cons, and the best choice will depend on factors such as the number of missing teeth, the condition of the remaining teeth, and personal preferences.
10. How much do dental bridges cost?
The cost of dental bridges varies depending on several factors, including the material used, the complexity of the procedure, and the location of the dental office. On average, dental bridges can cost between $500 to $1,500 per tooth.
-
Material Costs: Bridges made from porcelain or ceramic typically cost more than those made from metal or resin.
-
Type of Bridge: Implant-supported bridges tend to be more expensive due to the cost of dental implants.
-
Location: The cost may vary based on the geographical location and the expertise of the dentist.
It's essential to consult with your dentist for a detailed cost estimate and inquire about financing or payment plans if needed. Many dental offices offer flexible payment options or work with insurance companies to help make the procedure more affordable.


