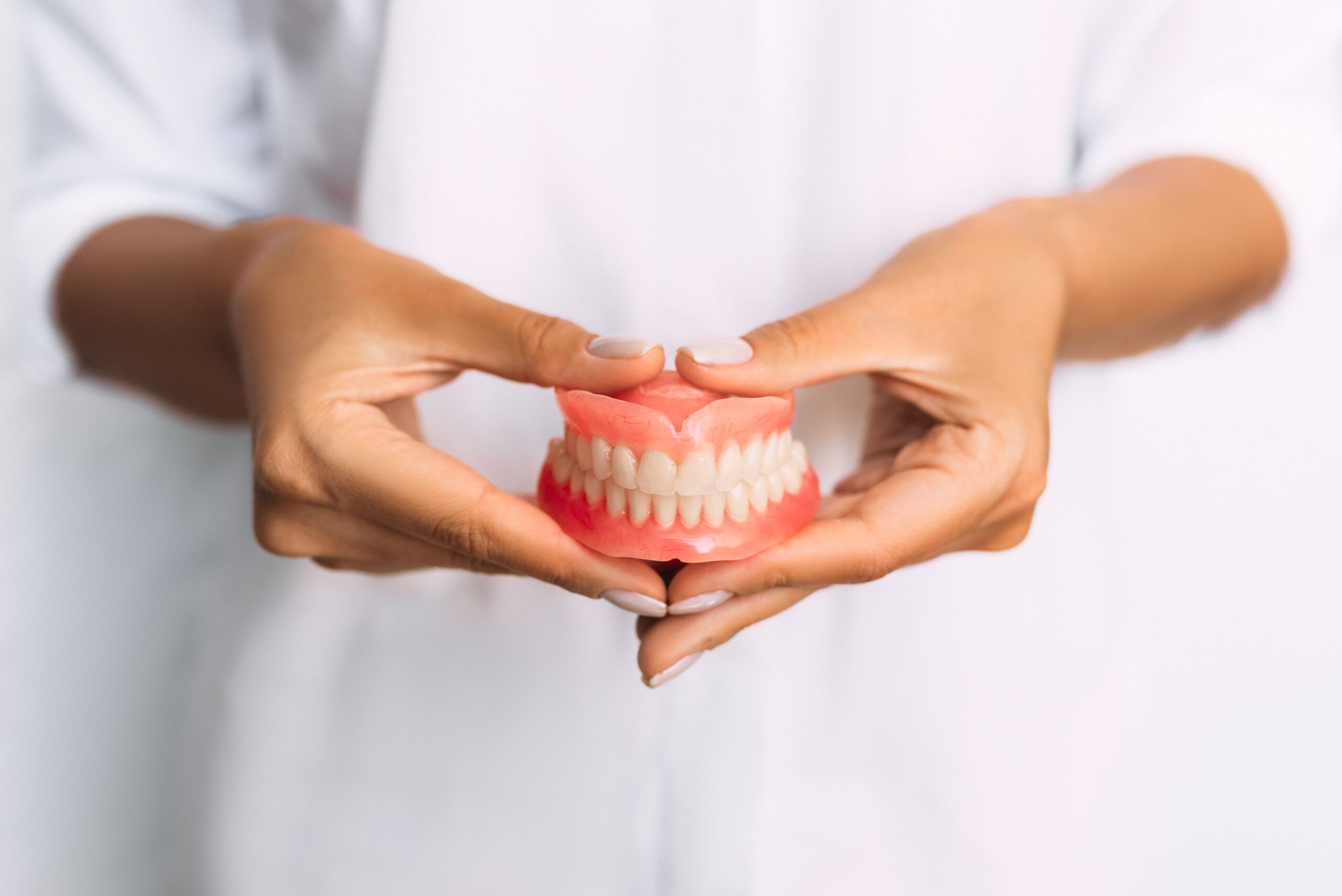
Introduction to Full Denture
A full denture is a removable prosthetic device used to replace a complete set of missing teeth. Full dentures are designed for patients who have lost all their teeth in one or both arches (upper and lower). Unlike partial dentures, which are used when some natural teeth remain, full dentures provide a complete solution for tooth loss, improving both aesthetics and functionality.
The main goal of full dentures is to restore the ability to eat, speak, and smile with confidence, while also preventing the changes to facial appearance caused by the loss of teeth. When teeth are missing, the face can appear sunken, and the cheeks and lips may lose volume. Full dentures help to restore a more youthful appearance by filling out the face and improving the shape of the smile.
Full dentures are custom-made to fit the shape of a patient's gums and jawbone, ensuring comfort and stability. They are typically made from materials such as acrylic resin, porcelain, or a combination of resin and metal to offer durability and functionality. Full dentures can be designed for the upper jaw, lower jaw, or both, depending on the extent of tooth loss.
Causes and Risk Factors of Full Dentures
The need for full dentures typically arises from several causes related to the loss of teeth. These causes can be either preventable or due to unavoidable factors, such as aging or disease. Understanding these causes and risk factors helps patients make informed decisions about their oral health and denture needs.
Common Causes of Tooth Loss:
-
Severe Tooth Decay:
-
Untreated tooth decay is one of the leading causes of tooth loss. When cavities are left untreated for a prolonged period, they can cause extensive damage to the tooth, eventually requiring extraction. Severe decay may also lead to infection in the root, necessitating full tooth removal and replacement with a denture.
-
-
Periodontal (Gum) Disease:
-
Gum disease, also known as periodontitis, is a leading cause of tooth loss, especially in adults. When plaque builds up on teeth and gums, it leads to inflammation and infection of the gum tissues. Over time, untreated gum disease can cause tooth mobility, which can eventually lead to the need for full dentures.
-
-
Trauma or Injury:
-
Accidents, falls, or injuries that result in broken or severely damaged teeth may lead to tooth loss. When trauma causes irreparable damage to a tooth, it may be necessary to remove the tooth and replace it with a full denture.
-
-
Aging:
-
As people age, the risk of losing teeth increases due to factors like wear and tear, tooth decay, and gum disease. Aging teeth may become weak or brittle and more prone to damage. Consequently, full dentures can provide a solution for individuals who have lost all their teeth with age.
-
-
Medical Conditions:
-
Certain medical conditions, such as diabetes, cancer, or autoimmune disorders, can negatively affect oral health and increase the likelihood of tooth loss. Additionally, medications such as chemotherapy drugs can affect the gums and teeth, leading to conditions that may necessitate the use of full dentures.
-
-
Genetics:
-
Some individuals may be genetically predisposed to conditions such as weak enamel or gum disease, which can make them more susceptible to tooth loss. Genetic factors can lead to premature tooth loss and may require full dentures at an earlier age than expected.
-
Risk Factors for Needing Full Dentures:
-
Poor Oral Hygiene: Inadequate brushing, flossing, and neglecting routine dental check-ups can lead to tooth decay, gum disease, and eventually tooth loss.
-
Tobacco Use: Smoking or using tobacco products can increase the risk of gum disease and tooth decay, which may result in tooth loss and the need for dentures.
-
Dietary Habits: A diet high in sugars, acids, and carbohydrates can contribute to tooth decay and gum disease. A poor diet may increase the risk of requiring dentures.
-
Teeth Grinding (Bruxism): Chronic teeth grinding, often due to stress, can wear down teeth and lead to fractures, which may result in the need for dentures.
Symptoms and Signs of Full Denture Issues
While full dentures can dramatically improve your quality of life, issues with fit, comfort, or function can arise over time. It's essential to recognize the symptoms and signs of potential issues to address them promptly.
Symptoms of Full Denture Issues:
-
Pain and Discomfort:
-
New denture wearers often experience some discomfort or irritation as they adjust to their new prosthetics. Ill-fitting dentures can cause sores or painful spots in the mouth, leading to discomfort during speaking or eating.
-
-
Loose or Slipping Dentures:
-
If your dentures don't fit properly, they may slip or move around in your mouth. This can make it difficult to speak clearly or chew food comfortably. Loose dentures may also cause embarrassment or self-consciousness.
-
-
Excessive Saliva Production:
-
Full dentures may cause an increase in saliva production, especially during the initial period of wearing them. While this is common, excessive salivation may indicate that the dentures are not fitting well.
-
-
Gum Irritation or Inflammation:
-
Gum irritation is common when new dentures are first worn, but it should subside with time. Persistent inflammation, soreness, or swelling could be a sign that your dentures need to be adjusted.
-
-
Difficulty Eating:
-
If you find it difficult to chew certain foods or experience pain while eating, it could indicate that your dentures are not fitting properly, causing discomfort or instability.
-
-
Changes in Speech:
-
When new dentures are first worn, they may affect the way you speak, especially with sounds like “s” or “f”. It may take time to adjust to the new feel of the dentures, but persistent speech difficulties may require adjustments.
-
Diagnosis of Full Dentures
The process of diagnosing the need for full dentures involves a thorough examination by a prosthodontist or a general dentist. The dentist will assess your oral health and determine whether full dentures are the best solution for your condition.
Step 1: Comprehensive Examination:
Your dentist will begin by performing a visual and physical examination of your gums, jawbone, and any remaining teeth. This helps them determine the overall health of your mouth and whether full dentures are needed.
Step 2: X-rays and Imaging:
X-rays are essential for understanding the structure of your jawbone, gums, and remaining teeth. The dentist will assess bone density and the health of your jaw to ensure that dentures will fit properly and comfortably.
Step 3: Impressions of Your Mouth:
Your dentist will take impressions of your gums and remaining teeth to create a set of custom dentures. Accurate impressions are essential for creating dentures that fit well and perform optimally.
Step 4: Discussion of Treatment Options:
Once the dentist has completed the examination and gathered the necessary information, they will discuss the various treatment options with you, including conventional full dentures, immediate dentures, and implant-supported dentures.
Treatment Options for Full Dentures
When it comes to replacing missing teeth with full dentures, there are several treatment options available, each with its own advantages and considerations.
Conventional Full Dentures:
Conventional full dentures are created after all remaining teeth have been extracted and the gums have fully healed. Healing may take several months, during which time the gums shrink and reshape. These dentures are made to fit the final shape of the gums and are designed for long-term use.
Immediate Full Dentures:
Immediate dentures are placed in the mouth immediately after tooth extraction. They allow patients to have teeth during the healing period, although adjustments are often necessary once the gums heal and shrink. These dentures provide a temporary solution until permanent dentures can be created.
Implant-Supported Dentures:
Implant-supported dentures are an advanced option for patients who have enough healthy bone to support dental implants. Dental implants are surgically placed into the jawbone, and the dentures are anchored to the implants. This offers a more stable, permanent solution compared to traditional removable dentures and can prevent further bone loss.
Overdentures:
Overdentures are similar to traditional dentures, but they are supported by either remaining natural teeth or dental implants. They are more stable than standard dentures and offer improved retention and function.
Prevention and Management of Full Dentures
Maintaining the health of your dentures and gums is critical to ensuring long-term success and comfort. Proper care can help prevent complications and prolong the lifespan of your dentures.
Prevention of Denture-Related Issues
-
Proper Denture Hygiene: Just like natural teeth, dentures require regular cleaning to prevent plaque buildup, staining, and bad breath. Clean your dentures daily with a soft brush and non-abrasive cleaner.
-
Regular Dental Check-ups: Regular visits to the dentist are essential for monitoring the fit of your dentures and checking for any signs of gum disease or oral infection.
-
Avoid Damage: Handle your dentures carefully to avoid cracking or bending. Remove them before sleeping and store them in a safe, moist environment.
-
Dietary Considerations: Avoid chewing excessively hard or sticky foods that can cause damage to dentures. Similarly, avoid foods and drinks that stain teeth (like coffee, tea, and red wine) to keep your dentures looking fresh.
Managing Denture Fit and Comfort:
-
Adjustment Appointments: Over time, your gums and jawbone may change shape, affecting how well your dentures fit. Your dentist may need to adjust the fit to ensure comfort and functionality.
-
Denture Adhesives: If your dentures feel loose, you can use denture adhesives to improve the fit. However, regular adjustments from your dentist are important for long-term comfort.
Complications of Full Dentures
While full dentures provide many benefits, there are potential complications that may arise during their use. It's important to address these issues as soon as possible to avoid discomfort or further problems.
Common Complications:
-
Discomfort or Soreness: New denture wearers may experience some soreness or irritation, especially in the first few weeks. This can be alleviated with proper adjustments.
-
Loose Dentures: Over time, your gums and jawbone may change, causing your dentures to become loose. This can be corrected with adjustments or by getting new dentures.
-
Gum Irritation: If dentures don't fit properly or if they rub against the gums, they can cause irritation or sores. Proper fitting and regular dental visits can help prevent this.
-
Staining: Just like natural teeth, dentures can become stained by food, drink, and tobacco use. Regular cleaning can help keep them looking fresh.
-
Difficulty Chewing: Some patients may find it difficult to chew certain foods, especially hard or sticky foods. It can take some time to get used to eating with dentures.
Living with Full Dentures
After receiving full dentures, many patients adjust to their new smile and restored functionality. However, ongoing care and attention are essential for long-term success.
Adjusting to Dentures:
-
Speech and Eating: It may take some time to adjust to speaking and chewing with dentures. Start with soft foods and practice speaking to get used to the feel of the dentures in your mouth.
Maintaining Good Oral Hygiene:
-
Even though full dentures replace natural teeth, it's essential to care for your gums and remaining natural teeth. Continue to brush your gums and tongue regularly to remove plaque and bacteria.
Long-Term Care:
-
Regular Check-ups: Continue visiting your dentist regularly to monitor the fit of your dentures, as well as to ensure the health of your gums and jawbone.
-
Comfort and Fit: If you experience any discomfort or issues with your dentures, contact your dentist immediately. They can make adjustments or provide solutions to improve the fit and comfort.
Top 10 Frequently Asked Questions about Full Dentures
1. What are full dentures?
Full dentures (also known as complete dentures) are removable dental appliances used to replace all of the teeth in either the upper or lower jaw. They are custom-made to fit snugly over the gums and help restore both the function and appearance of the mouth. Full dentures are typically recommended when a person has lost all their natural teeth due to decay, disease, or injury.
2. How are full dentures made?
Full dentures are custom-made using impressions of your mouth. The process generally involves:
-
Initial Impressions: Your dentist will take impressions of your gums and any remaining teeth (if applicable). These impressions help create a mold of your mouth.
-
Model Creation: A model or wax replica of the denture is created, allowing your dentist to adjust the fit, color, and shape of the teeth to match your natural smile.
-
Final Fitting: Once the model is approved, the final denture is created from durable materials like acrylic or resin. Your dentist will then ensure the denture fits comfortably before finalizing the procedure.
The entire process can take several weeks, with a few visits to ensure a proper fit.
3. How long does it take to get used to full dentures?
It typically takes several days to a few weeks to get used to wearing full dentures. During this time, you may experience slight discomfort, difficulty chewing, or speaking. These sensations should gradually lessen as your mouth adjusts to the dentures. It's important to follow your dentist's instructions and have follow-up appointments to ensure proper fit and comfort.
4. Are full dentures comfortable to wear?
While full dentures may feel slightly uncomfortable at first, they should gradually become more comfortable as you adjust to them. Initially, you may experience sore spots or slight irritation, but this is normal as your gums get used to the dentures. Your dentist can make adjustments to ensure the best possible fit. Over time, dentures should feel natural and allow you to eat and speak more easily.
5. How do I take care of my full dentures?
Proper care is essential to maintaining your full dentures and keeping them clean. Here are some tips:
-
Clean your dentures daily: Brush your dentures with a soft brush and non-abrasive toothpaste or a special denture cleaner to remove plaque and food particles.
-
Rinse after eating: Rinse your dentures with water after eating to remove any food debris.
-
Soak overnight: When not in use, store your dentures in a water-based denture cleanser solution or plain water to prevent them from drying out or losing their shape.
-
Regular check-ups: Visit your dentist regularly to have your dentures professionally cleaned and adjusted as needed.
6. Can full dentures improve my ability to eat and speak?
Yes, full dentures can significantly improve your ability to eat and speak. Initially, you may need time to adapt to chewing and pronouncing words with your new dentures. However, as your mouth gets accustomed to the dentures, you should find it easier to chew a variety of foods and speak more clearly. Your dentist can make adjustments to your dentures to help improve your comfort and function.
7. Will I need to replace my full dentures?
Yes, full dentures typically need to be replaced every 5 to 10 years, depending on factors such as wear, changes in your mouth, and the condition of the dentures. Over time, the shape of your gums and jawbone may change, causing the dentures to fit less snugly. Regular adjustments by your dentist can help extend the life of your dentures, but a replacement may eventually be necessary to ensure proper fit and comfort.
8. Can I still eat all foods with full dentures?
While full dentures restore much of your ability to eat, you may need to make some adjustments to your diet. It may take some time to get used to chewing harder or stickier foods. Some foods, like nuts, hard candies, or chewy meats, may be more challenging to eat with dentures. You may need to cut foods into smaller pieces or avoid certain items. Your dentist will offer advice on which foods are best for your dentures and mouth.
9. Can I wear my full dentures while sleeping?
It's generally recommended not to wear full dentures while sleeping. Removing your dentures at night gives your gums a chance to rest and prevents irritation or infections caused by trapped moisture. It also helps prevent damage to the dentures themselves. You should remove your dentures at night, clean them thoroughly, and store them in water or a denture solution to keep them in good condition.
10. How much do full dentures cost?
The cost of full dentures can vary widely based on factors such as the materials used, the complexity of the case, and geographic location. On average, the cost of full dentures ranges from $1,000 to $3,000 per arch (upper or lower). The total cost may include follow-up visits, adjustments, and any additional procedures such as extractions. Some dental insurance plans may help cover the cost of dentures, but coverage varies. It's important to discuss payment options and financing with your dentist before starting the treatment.


