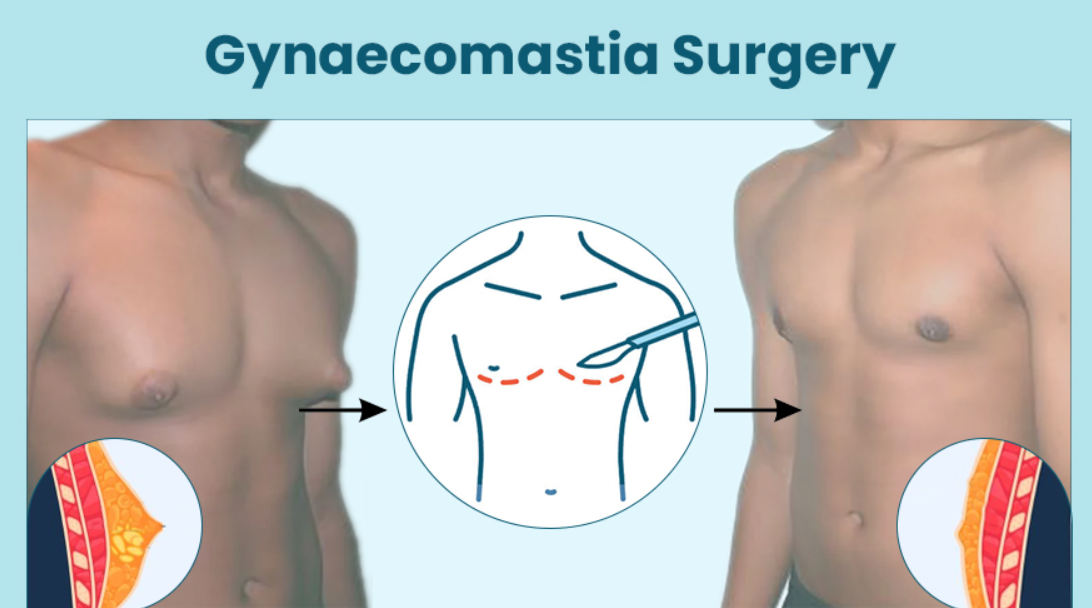
Introduction to Gynecomastia Correction
Gynecomastia is a condition characterized by enlarged breast tissue in men, causing a more feminine chest appearance. While it is not inherently dangerous, gynecomastia can cause significant emotional distress, embarrassment, and self-esteem issues. The condition can affect one or both breasts and may result from hormonal imbalances, medical conditions, medications, or lifestyle factors.
Gynecomastia correction is a cosmetic surgical procedure designed to reduce excess breast tissue, creating a flatter, more masculine chest contour. The procedure is one of the most common aesthetic surgeries performed for men and has gained widespread popularity as more individuals seek to address the physical and psychological effects of the condition.
In this guide, we will explore gynecomastia correction in detail, including its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, and complications. Additionally, we will provide comprehensive information on post-surgery care and prevention, helping individuals better understand their treatment options and the long-term management of the condition.
Causes and Risk Factors of Gynecomastia
The development of gynecomastia is caused by an imbalance of estrogen (a hormone typically associated with female characteristics) and testosterone (the male sex hormone). This hormonal imbalance can occur for various reasons, affecting men at different stages of life. Let's explore the primary causes and risk factors for gynecomastia:
1. Hormonal Imbalance
The most common cause of gynecomastia is a hormonal imbalance between estrogen and testosterone. Estrogen stimulates the development of breast tissue, while testosterone prevents excessive growth. When there is a relative increase in estrogen levels or a decrease in testosterone levels, the breast tissue can grow abnormally, resulting in gynecomastia.
-
Puberty: Hormonal changes during puberty often cause temporary gynecomastia. In most cases, this resolves on its own within a few months or years as hormone levels stabilize.
-
Aging: As men age, testosterone levels naturally decline, leading to an increased risk of gynecomastia. Older men may also experience an increase in fat accumulation, which can make the breast tissue appear more prominent.
2. Medications
Certain medications can contribute to gynecomastia by altering the hormonal balance or increasing estrogen activity in the body. Common medications that can cause gynecomastia include:
-
Anti-androgens: Used to treat prostate enlargement or male pattern baldness.
-
Anabolic Steroids: Often used by bodybuilders to increase muscle mass, these can affect hormonal levels and cause breast tissue development.
-
Certain Antibiotics: Some antibiotics, like isoniazid, can affect testosterone levels and lead to gynecomastia.
-
Heart Medications: Medications like calcium channel blockers or digoxin can contribute to hormonal imbalances.
-
Antidepressants: Certain antidepressants, such as tricyclics, can cause gynecomastia.
3. Obesity
Excess body fat, especially in the chest area, can contribute to the appearance of gynecomastia. Obesity leads to increased production of estrogen, the hormone responsible for the development of breast tissue. In some cases, gynecomastia in overweight men is more related to the accumulation of fat (called pseudogynecomastia) rather than glandular tissue.
4. Medical Conditions
Several medical conditions can contribute to the development of gynecomastia:
-
Liver Disease: Chronic liver disease, such as cirrhosis, can cause gynecomastia by disrupting the body's ability to process hormones properly.
-
Hyperthyroidism: Overactive thyroid glands can lead to hormonal imbalances and contribute to gynecomastia.
-
Testicular Tumors: Tumors in the testes can secrete estrogen-like hormones, resulting in gynecomastia.
-
Kidney Failure: Men undergoing dialysis for kidney failure are at an increased risk of developing gynecomastia.
-
Klinefelter Syndrome: A genetic condition that affects male sex chromosomes, leading to abnormal breast tissue development.
5. Substance Use
The use of alcohol and certain drugs, including marijuana, heroin, and amphetamines, can cause gynecomastia. These substances affect the body’s ability to regulate hormones, increasing the likelihood of developing enlarged breast tissue.
6. Genetics
In some cases, gynecomastia is hereditary, and men with a family history of the condition may be more prone to developing it. Genetic predispositions can affect how the body processes hormones, leading to an increased risk of gynecomastia.
Symptoms and Signs of Gynecomastia Correction
Gynecomastia correction refers to the treatment or surgical intervention for the condition known as gynecomastia, where there is an abnormal enlargement of male breast tissue. It’s important to note that gynecomastia itself is a medical condition, and the term "correction" refers to the treatment options for it. Below are some key symptoms and signs that may indicate the need for gynecomastia correction:
1. Enlarged Breast Tissue
The most prominent symptom of gynecomastia is enlarged breast tissue in one or both breasts. The enlargement may be symmetrical or asymmetrical, affecting one side of the chest more than the other.
2. Tenderness or Pain
Many men with gynecomastia experience painful or tender breasts, particularly when the area is touched or pressure is applied. This discomfort is due to the swelling of the glandular tissue and is often more noticeable during physical activity or while lying on the stomach.
3. Changes in the Nipple Area
-
Enlarged Areola: The area around the nipple, known as the areola, may become enlarged or more pronounced.
-
Nipple Sensitivity: The nipple may become more sensitive or painful in some cases, especially when touched.
4. Uneven Chest Appearance
Gynecomastia can cause uneven chest contours, where one breast may be larger than the other, leading to asymmetry. This unevenness can be particularly noticeable when wearing tight clothing or when engaging in physical activities.
5. Emotional and Psychological Impact
For many men, gynecomastia can lead to psychological distress, including embarrassment, self-consciousness, and low self-esteem. Men with gynecomastia may avoid social situations, public swimming pools, or dressing rooms due to the perceived stigma associated with the condition.
Diagnosis of Gynecomastia Correction
Gynecomastia is a condition where men develop enlarged breast tissue, often due to hormonal imbalances. Early diagnosis is crucial to identify the underlying cause and guide appropriate treatment. Here's how gynecomastia is diagnosed:
1. Medical History
-
A thorough medical history is taken to understand any underlying health conditions, medications, or lifestyle factors contributing to the condition.
-
It includes questions about any use of anabolic steroids, marijuana, or other substances.
2. Physical Examination
-
A healthcare provider will conduct a physical exam to assess the size, consistency, and tenderness of the breast tissue.
-
The exam may help distinguish between true gynecomastia (enlarged breast tissue) and pseudogynecomastia (fat accumulation).
3. Blood Tests
-
Blood tests may be ordered to check hormone levels, including estrogen, testosterone, and prolactin, to identify any hormonal imbalances.
4. Imaging Tests
-
Ultrasound or mammography may be used to examine the tissue more closely and rule out other possible causes like breast cancer.
5. Biopsy
-
In some cases, if there is a suspicion of a tumor, a biopsy may be performed to check for abnormal tissue.
Treatment Options for Gynecomastia Correction
The treatment of gynecomastia depends on the severity of the condition, its cause, and the patient's preferences. The available treatment options include:
1. Medications
In cases where gynecomastia is caused by hormonal imbalance, medications such as Selective Estrogen Receptor Modulators (SERMs) or Aromatase Inhibitors may be prescribed to help balance hormone levels and reduce the growth of breast tissue.
2. Liposuction
For pseudogynecomastia (fatty enlargement of the breast), liposuction is a common treatment. This minimally invasive procedure removes excess fat from the chest using a small tube and suction device. Liposuction is ideal for men with no glandular tissue enlargement but excess fat in the chest area.
3. Mastectomy (Glandular Tissue Removal)
For true gynecomastia, where excess glandular tissue is the primary cause of enlargement, mastectomy (removal of glandular tissue) is the most effective surgical option. This procedure is performed by making small incisions around the nipple area, through which the excess tissue is removed.
4. Combination of Liposuction and Mastectomy
In many cases, a combination of liposuction and mastectomy is performed to address both fat and glandular tissue. This ensures a comprehensive and permanent solution to gynecomastia.
5. Post-Surgery Care
After surgery, patients are typically required to wear a compression garment to help minimize swelling and promote proper healing. Recovery times vary depending on the surgical approach, but most men can return to light activities within 1-2 weeks and full physical activity within 4-6 weeks.
Prevention and Management of Gynecomastia Correction
Gynecomastia, the condition of enlarged male breast tissue, can be a source of significant emotional and physical discomfort for many men. It is important to recognize that while prevention may not always be entirely possible due to genetic or hormonal factors, effective management strategies can help reduce the severity of the condition and prevent its recurrence after correction. Below are the key aspects of prevention and management of gynecomastia:
1. Healthy Lifestyle
Maintaining a healthy weight through balanced nutrition and regular exercise can help prevent pseudogynecomastia. A healthy diet rich in nutrients and low in processed foods can also contribute to balanced hormone levels.
2. Avoiding Drugs and Alcohol
Minimizing or eliminating the use of drugs, especially steroids, alcohol, and recreational drugs like marijuana, can significantly reduce the risk of gynecomastia.
3. Regular Check-ups
Routine check-ups with a doctor can help monitor hormone levels and identify any underlying conditions that may contribute to gynecomastia. Early diagnosis and intervention are key to preventing further development of the condition.
Complications of Gynecomastia Correction
Gynecomastia correction, which involves surgical or non-surgical interventions to treat enlarged male breasts, can significantly enhance self-esteem and quality of life. However, as with any surgical procedure, there are potential risks and complications that patients should be aware of before deciding to undergo the treatment. Here, we discuss the common complications associated with gynecomastia correction.
1. Scarring
Small scars are common after surgery, but they are typically well-hidden around the nipple or in the natural chest folds. Scarring is generally minimal and fades over time.
2. Infection
Although rare, infection is a potential complication after gynecomastia surgery. It can usually be controlled with antibiotics if caught early.
3. Asymmetry
In some cases, the chest may appear slightly uneven after surgery, though this can usually be corrected with revision surgery if necessary.
4. Numbness or Sensitivity Changes
Temporary numbness or altered sensitivity in the nipples or chest may occur, but these changes typically resolve as the body heals.
Living with the Condition of Gynecomastia Correction
Living with gynecomastia, the condition of enlarged male breast tissue, can affect one's self-esteem and confidence. Surgical correction offers a lasting solution, but the journey doesn't end with the procedure. Here's how to manage life after gynecomastia surgery:
-
Post-Surgery Recovery:
After surgery, swelling and bruising are common but usually subside within a few weeks. Wearing compression garments helps reduce swelling and supports healing. Most people can return to normal activities in a few weeks, with heavy exercises avoided for a month or so. -
Emotional Relief:
Many individuals report a boost in confidence and body image after surgery, feeling more comfortable in social situations and physical activities like swimming. -
Ongoing Care:
Regular follow-up appointments with your surgeon are important to ensure proper healing. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle with balanced nutrition and light exercise can prevent recurrence of the condition. -
Mental Health Support:
If you struggled with insecurity due to gynecomastia, consider seeking support from a therapist or support group to address any lingering anxiety or stress.
Top 10 Frequently Asked Questions about Gynecomastia Correction
1. What is gynecomastia, and why does it occur?
Gynecomastia is the benign enlargement of male breast tissue, often resulting from hormonal imbalances between estrogen and testosterone. It can affect one or both breasts and is common during puberty, but it can also occur in adults due to factors like obesity, certain medications, anabolic steroid use, or underlying health conditions such as liver disease or hyperthyroidism.
2. How is gynecomastia surgery performed?
Gynecomastia correction typically involves a combination of liposuction and excision techniques:
-
Liposuction: Removes excess fatty tissue through small incisions.
-
Excision: Removes glandular tissue and excess skin, particularly in cases with significant tissue enlargement or sagging.
The procedure is usually performed under general anesthesia on an outpatient basis.
3. What is the recovery process like?
Post-surgery, patients may experience swelling, bruising, and mild discomfort, which can be managed with prescribed medications. Most individuals can return to work within a few days, avoiding strenuous activities for about 4–6 weeks. Wearing a compression garment is typically recommended for 4–6 weeks to support healing and reduce swelling.
4. Are there risks or complications associated with the surgery?
While gynecomastia surgery is generally safe, potential risks include:
-
Infection or bleeding
-
Scarring
-
Asymmetry
-
Changes in nipple sensation
-
Skin irregularities
Choosing a board-certified plastic surgeon can minimize these risks.
5. How long do the results last?
The results of gynecomastia surgery are typically permanent. However, significant weight gain, hormonal imbalances, or the use of certain substances like anabolic steroids can lead to recurrence. Maintaining a stable weight and healthy lifestyle is crucial for long-term results.
6. Will insurance cover the cost of the surgery?
Insurance coverage for gynecomastia surgery varies. In some cases, if the condition causes physical discomfort or pain, insurance may cover part of the cost. It's essential to consult with your insurance provider and surgeon to determine coverage and potential out-of-pocket expenses.
7. At what age is gynecomastia surgery appropriate?
Gynecomastia surgery is generally recommended for individuals over 18 years of age, once breast development has stabilized. However, in certain cases, surgery may be considered earlier if the condition causes significant physical or emotional distress.
8. What should I expect during the consultation?
During the consultation, the surgeon will:
-
Review your medical history and conduct a physical examination
-
Discuss your goals and expectations
-
Explain the surgical options and techniques
-
Provide information on risks, recovery, and costs
-
Take photographs for medical records
This is an opportunity to ask questions and ensure you are fully informed before proceeding.
9. Can gynecomastia recur after surgery?
While rare, gynecomastia can recur if the underlying causes are not addressed, such as continued use of substances that affect hormone levels or significant weight gain. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle and following post-operative care instructions are vital to prevent recurrence.
10. How do I choose the right surgeon?
Selecting a qualified surgeon is crucial for achieving optimal results:
-
Board Certification: Ensure the surgeon is certified by a recognized board in plastic or reconstructive surgery.
-
Experience: Look for a surgeon with extensive experience in gynecomastia surgery.
-
Before-and-After Photos: Review the surgeon's portfolio of previous patients.
-
Consultation: Schedule a consultation to discuss your goals, ask questions, and assess your comfort level with the surgeon.


