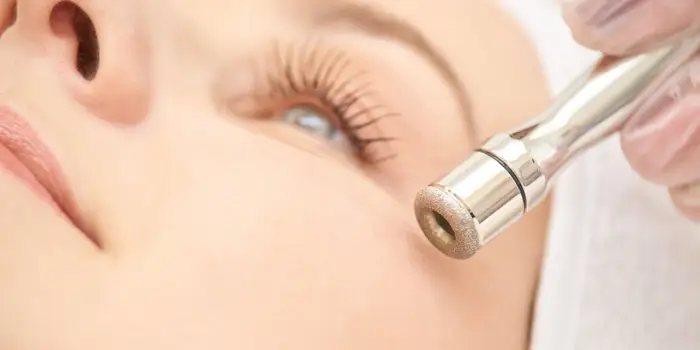
Introduction to Dermabrasion
Dermabrasion is a surgical skin resurfacing technique designed to improve the appearance and texture of the skin by removing its damaged outer layers. It is performed using a rapidly rotating device (such as a wire brush or diamond wheel) that gently abrades the skin's surface, promoting the regeneration of smoother, healthier tissue.
The procedure is particularly effective for reducing acne scars, surgical scars, wrinkles, age spots, tattoos, and sun damage. By removing the epidermis and part of the dermis, dermabrasion triggers the body's natural healing process, encouraging the formation of new collagen and rejuvenated skin.
Dermabrasion is distinct from less invasive procedures like microdermabrasion or chemical peels - it penetrates deeper into the skin layers and is typically performed under local or general anesthesia by a dermatologic surgeon or plastic surgeon.
This technique was first introduced in the 1950s but has evolved significantly with modern equipment, better anesthesia, and improved infection control measures. Today, dermabrasion is used not only for cosmetic enhancement but also for medical conditions such as actinic keratosis (precancerous lesions), post-traumatic scars, and certain pigmentation disorders.
Its goal is not only aesthetic refinement but also psychological confidence restoration for patients with disfiguring scars or texture irregularities. With careful planning, experienced execution, and proper aftercare, dermabrasion offers visible rejuvenation, smoother skin, and long-lasting results.
Causes and Risk Factors for Dermabrasion
While dermabrasion is a treatment rather than a disease, it is indicated for conditions that cause surface irregularities or scarring of the skin. The "causes" in this context refer to the underlying skin conditions prompting the need for dermabrasion.
A. Common Causes (Indications for Dermabrasion)
-
Acne Scarring:
Deep or pitted acne scars (ice-pick or boxcar scars) are among the most common indications. Dermabrasion smooths the surface and reduces shadowing. -
Surgical or Traumatic Scars:
Improves the contour of scars resulting from surgery, burns, or accidents. -
Fine Wrinkles and Aging Lines:
Especially around the mouth and eyes due to sun damage or natural aging. -
Hyperpigmentation and Sun Damage:
Reduces uneven pigmentation, age spots, and photodamage. -
Actinic Keratoses:
Removes precancerous sun-induced lesions on the face and scalp. -
Tattoos:
Occasionally used to fade or remove superficial tattoos. -
Rhinophyma (Severe Rosacea):
Contours thickened nasal skin caused by chronic rosacea.
B. Risk Factors Affecting Dermabrasion Outcomes
While the procedure is generally safe, some factors increase the risk of complications or affect healing:
-
Skin Tone: Darker skin types (Fitzpatrick IV-VI) are prone to post-inflammatory pigmentation changes.
-
Active Acne or Infections: Bacterial, viral (especially herpes simplex), or fungal infections can worsen after dermabrasion.
-
Recent Isotretinoin Use: Use of isotretinoin (Accutane) within 6-12 months increases risk of scarring.
-
Keloid-Prone Individuals: History of abnormal scar formation may lead to hypertrophic scars.
-
Bleeding Disorders or Anticoagulant Use: Increase risk of postoperative bleeding.
-
Smoking and Alcohol Use: Impair circulation and delay healing.
-
Excessive Sun Exposure: May increase sensitivity and risk of pigment irregularities.
Careful patient screening and preoperative counseling are vital for safe, predictable outcomes.
Symptoms and Signs Related to Conditions Treated by Dermabrasion
The symptoms prompting a person to seek dermabrasion usually relate to skin texture irregularities, discoloration, or scarring. While not painful conditions themselves, they can cause physical discomfort or emotional distress.
Common Skin Changes
-
Uneven Skin Texture: Bumpy, rough, or pitted surfaces from acne or injury.
-
Visible Scars: Shallow or deep scars that affect facial harmony.
-
Fine Lines and Wrinkles: Early aging changes around the eyes, lips, and forehead.
-
Pigment Irregularities: Dark spots, freckles, or blotchy complexion.
-
Thickened or Enlarged Pores: Often due to chronic acne or sebaceous gland hypertrophy.
Associated Emotional and Psychological Signs
-
Low Self-Esteem: Especially in individuals with visible facial scarring.
-
Social Anxiety or Avoidance: Reluctance to engage in public or professional settings.
-
Body Image Concerns: Persistent dissatisfaction with appearance.
Dermabrasion addresses not only physical irregularities but also the emotional burden caused by visible skin imperfections, making it a holistic aesthetic and reconstructive intervention.
Diagnosis and Pre-Procedural Evaluation
Before performing dermabrasion, a detailed dermatological and medical evaluation is essential to ensure that the patient is a suitable candidate and to plan the depth and extent of treatment.
A. Medical History
-
Review of medical conditions (diabetes, bleeding disorders, autoimmune diseases).
-
History of cold sores (herpes simplex), since dermabrasion may reactivate dormant infection.
-
Use of medications such as isotretinoin, steroids, or anticoagulants.
-
Previous cosmetic treatments (chemical peels, laser therapy, fillers).
B. Physical Examination
-
Skin assessment: texture, thickness, pigmentation, and presence of scars or infections.
-
Determination of skin type using the Fitzpatrick scale to predict pigmentation risks.
-
Evaluation of scar depth, location, and direction relative to natural skin folds.
C. Diagnostic Tests (if needed)
-
Skin Culture or Viral Screening: For suspected infections.
-
Allergy Patch Test: If topical anesthesia or antiseptics are used.
D. Pre-Procedure Counseling
-
Realistic discussion about expected results, possible redness, peeling, or downtime.
-
Avoidance of sun exposure, tanning, and harsh skincare products before the procedure.
-
Discontinuation of retinoids, aspirin, and blood thinners 1-2 weeks before treatment.
Treatment Options and Procedure Details
Treatment options for severe wounds and burns integrate advanced surgical procedures-primarily debridement, escharotomy, and skin grafting-along with supportive therapies to restore form, function, and reduce complications. The procedures are chosen based on the burn depth, extent, and presence of infection or vascular compromise.
A. The Dermabrasion Procedure
-
Anesthesia:
Local anesthesia with sedation or general anesthesia depending on the treatment area. -
Skin Preparation:
The area is cleansed, degreased, and marked for uniform abrasion. -
Abrasive Device:
A high-speed handpiece fitted with a diamond fraise or wire brush is used to gently remove the outer layers of the skin. -
Controlled Depth Removal:
The surgeon removes damaged epidermis and superficial dermis until uniform bleeding indicates the right depth. -
Cooling and Dressing:
A cool saline compress is applied, followed by a sterile, non-stick dressing.
The procedure typically lasts 30-90 minutes, depending on the size of the treatment area.
B. Modern Variations and Alternatives
-
Microdermabrasion: A milder, non-invasive form using crystals or diamond tips - suitable for superficial rejuvenation.
-
Laser Resurfacing: CO₂ or Er:YAG lasers can replace traditional dermabrasion for precision.
-
Combination Treatments: Dermabrasion followed by chemical peel or platelet-rich plasma (PRP) enhances collagen regeneration.
C. Postoperative Care
-
Keep dressing moist and clean for 3-5 days.
-
Avoid makeup, sun exposure, or scrubbing for 2-3 weeks.
-
Use broad-spectrum sunscreen daily to prevent pigmentation.
-
Healing occurs over 7-14 days, with redness fading over weeks.
Prevention and Management of Dermabrasion
Prevention and management of dermabrasion focus on thorough preparation, proper post-procedure wound care, and early intervention to reduce complications such as infection, scarring, and pigment changes. Adhering to best practices ensures optimal healing and cosmetic outcomes.
Preventive Measures Before and After Dermabrasion
-
Pre-Treatment Skin Conditioning: Use of retinoids or hydroquinone for 4 weeks improves results and minimizes pigmentation risk.
-
Avoid Isotretinoin: Wait at least 6-12 months after isotretinoin therapy to avoid hypertrophic scarring.
-
Sun Protection: Sunscreen use before and after is mandatory.
-
Avoid Smoking: Enhances blood circulation and healing.
Management After Procedure
-
Gentle Skin Care: Use mild cleansers and moisturizers.
-
Cold Compresses: Reduce swelling and redness.
-
Antiviral or Antibiotic Medication: Prevent secondary infections.
-
Avoid Picking or Scratching: Prevents scarring and pigment changes.
-
Follow-Up Visits: Regular checkups ensure proper healing and early detection of complications.
Complications of Dermabrasion
The main complications of dermabrasion include both transient side effects and less common-but potentially serious-risks. Awareness, careful patient selection, and diligent aftercare help reduce these outcomes.
Early (Short-Term) Complications
-
Swelling, Redness, and Oozing: Common in first few days; subsides with care.
-
Infection: Bacterial or viral (herpes simplex) infections can delay healing.
-
Pain and Burning Sensation: Managed with analgesics and cool compresses.
Late (Long-Term) Complications
-
Hyperpigmentation or Hypopigmentation: Especially in darker skin tones.
-
Scarring: Hypertrophic or keloid scars in predisposed individuals.
-
Persistent Redness: May last for weeks due to increased vascularity of healing skin.
-
Texture Irregularities: Uneven abrasion may cause patchy results.
Proper patient selection and postoperative care greatly minimize these risks.
Living with the Condition and Post-Treatment Lifestyle
Living after dermabrasion-a resurfacing procedure for scars, wrinkles, or skin irregularities-demands attentive aftercare and lifestyle adjustments to promote healing, minimize complications, and protect your renewed skin.
A. The Healing Process
-
The skin gradually regenerates over 1-2 weeks, with continued collagen remodeling for up to 6 months.
-
Redness may persist temporarily but fades to reveal smoother, rejuvenated skin.
-
Regular moisturizing and sun protection are critical to maintain results.
B. Emotional and Aesthetic Benefits
-
Many patients experience renewed confidence and emotional relief after visible scars or pigmentation irregularities are minimized.
-
Improved self-image can significantly enhance social and professional interactions.
C. Long-Term Maintenance
-
Continue daily sunscreen (SPF 30+).
-
Use gentle skincare and avoid abrasive exfoliants.
-
Periodic touch-ups or maintenance treatments (microdermabrasion or laser) can extend results.
-
Maintain a balanced diet rich in vitamins A, C, and E for healthy skin regeneration.
Top 10 Frequently Asked Questions about Dermabrasion
1. What is Dermabrasion?
Dermabrasion is a cosmetic procedure that uses a specialized instrument to resurface and exfoliate the outer layers of the skin. It is designed to improve skin texture, reduce scars, fine lines, wrinkles, and pigmentation irregularities, and promote the growth of smoother, more youthful-looking skin.
2. What conditions can Dermabrasion treat?
Dermabrasion is commonly used for:
-
Acne scars and surgical scars
-
Fine wrinkles around the eyes and mouth
-
Sun-damaged skin
-
Age spots or uneven pigmentation
-
Rough skin texture
It is most effective for superficial to moderately deep skin imperfections.
3. How is Dermabrasion performed?
-
The skin is first numbed with local anesthesia or sedation.
-
A rotating brush or diamond wheel is used to carefully remove the top layers of the skin.
-
The depth of abrasion is controlled to target the problem areas without damaging underlying tissue.
-
After the procedure, a protective ointment and dressing are applied to aid healing.
A single session usually takes 30 minutes to 2 hours, depending on the treated area.
4. Is Dermabrasion painful?
Dermabrasion can be uncomfortable without anesthesia. Most patients experience minimal pain during the procedure if local anesthesia or sedation is used. Post-procedure, patients may feel redness, tightness, or mild stinging, which can last for several days.
5. What is the recovery time after Dermabrasion?
-
First 1-3 days: Redness, swelling, and minor oozing are common.
-
Days 4-7: Scabs form and gradually peel off.
-
1-2 weeks: Skin begins to reveal smoother, pinkish new tissue.
-
Full recovery: Typically within 2-4 weeks, depending on the depth of treatment and individual healing.
Sun protection is crucial during recovery to prevent pigmentation changes.
6. Are there risks and side effects?
Dermabrasion is generally safe but carries potential risks:
-
Redness, swelling, or irritation
-
Infection if the area is not kept clean
-
Temporary or permanent changes in skin pigmentation
-
Scarring in rare cases
-
Prolonged redness or sensitivity
Following post-procedure care instructions reduces these risks.
7. Who is a good candidate for Dermabrasion?
Ideal candidates are:
-
Adults with healthy skin without active infections or inflammatory skin conditions
-
Individuals with superficial to moderately deep scars, wrinkles, or sun damage
-
Those who have realistic expectations about the results
People with dark skin tones, active acne, or certain skin disorders should consult a dermatologist to assess suitability.
8. How many Dermabrasion sessions are required?
-
For mild skin issues, one session may be sufficient.
-
For deeper scars or extensive sun damage, 2-3 sessions spaced several weeks apart may be recommended.
-
The number of treatments depends on skin type, condition severity, and desired results.
9. How long do results last?
-
Results can last several years, but aging, sun exposure, and lifestyle factors influence longevity.
-
Proper skincare, moisturization, and sun protection help maintain the results.
-
Some patients may require touch-up treatments to maintain optimal skin appearance.
10. How should I prepare for Dermabrasion?
Preparation includes:
-
Avoiding tanning, retinoids, or harsh exfoliants for at least a week before the procedure
-
Discussing medications and medical history with the dermatologist
-
Arranging for post-procedure care, such as applying ointments and protecting skin from sun exposure
-
Understanding the healing process, downtime, and aftercare instructions
Following these steps ensures optimal results and minimizes complications.


