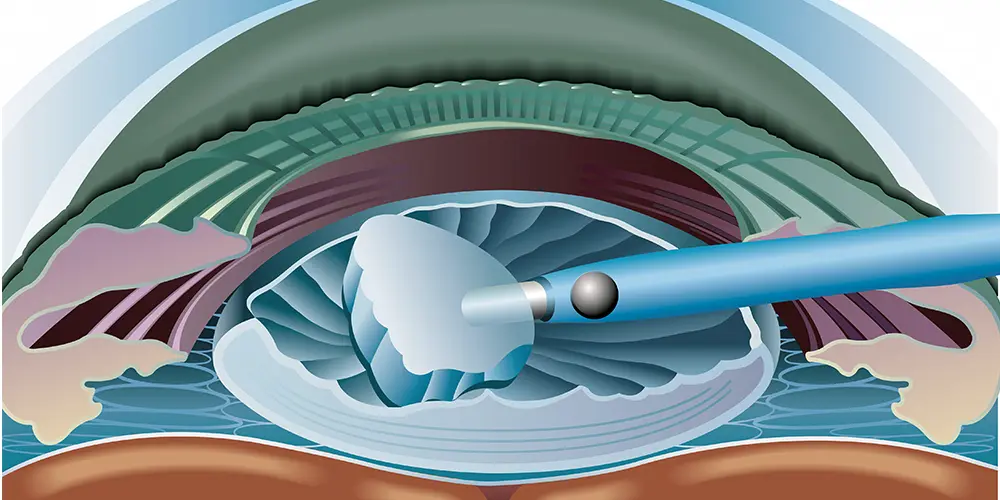
Introduction to Phaco With Foldable IOL
Phaco with Foldable IOL refers to the modern and widely preferred technique of cataract surgery where the cloudy natural lens is removed through phacoemulsification, and a foldable intraocular lens (IOL) is implanted through a micro-incision. This combination represents the most advanced form of cataract treatment, offering faster recovery, minimal surgical trauma, and significantly improved visual outcomes compared to older extracapsular or intracapsular cataract surgeries. The foldable IOL is a special lens that can be inserted through a tiny 2-3 mm incision using an injector system, where it unfolds naturally into the capsular bag. This reduces the need for large sutured incisions and lowers the risk of astigmatism.
Phaco with Foldable IOL has become the gold standard due to its precision, safety, and excellent outcomes. The technique integrates high-frequency ultrasound, advanced fluidics, minimally invasive incisions, and state-of-the-art lens technology. It is performed under topical or local anesthesia, allowing patients to remain comfortable and recover more quickly. Modern IOLs provide options for correcting refractive errors, astigmatism, and even presbyopia. As a result, many patients achieve spectacle-free vision after surgery, making this procedure not only rehabilitative but also visually enhancing.
Causes and Risk Factors of Conditions Requiring Phaco With Foldable IOL
Phaco with Foldable IOL is performed primarily to treat cataracts, a condition in which the natural lens becomes cloudy. Cataracts may develop due to multiple factors:
Causes
-
Age-related degeneration: The most common cause; natural proteins in the lens break down with age.
-
Diabetes mellitus: Increases the rate of cataract formation due to metabolic stress.
-
Trauma: Blunt or penetrating injuries accelerate lens opacification.
-
Prolonged steroid use: Systemic or topical steroids increase the risk of posterior subcapsular cataracts.
-
Congenital factors: Inherited disorders, metabolic diseases, or developmental abnormalities.
-
UV radiation exposure: Long-term exposure to sunlight accelerates oxidative damage to the lens.
-
Inflammatory eye conditions: Uveitis and chronic inflammation disrupt lens metabolism.
Risk Factors
-
Smoking, excessive alcohol use, obesity, malnutrition
-
Systemic diseases like hypertension and dyslipidemia
-
Pre-existing ocular diseases like glaucoma, keratopathy, or retinal disorders
-
Occupational exposure to heat, radiation, or bright light
-
Previous ocular surgery or trauma
These factors influence the timing, complexity, and expected outcomes of phacoemulsification.
Symptoms and Signs Requiring Phaco With Foldable IOL
Patients needing Phaco with Foldable IOL typically report a gradual decline in vision due to cataracts. Symptoms include:
Symptoms
-
Blurred or hazy vision interfering with daily activities
-
Difficulty reading, driving at night, or recognizing faces
-
Increased sensitivity to bright lights, glare, and halos
-
Dull or faded perception of colors
-
Frequent changes in glasses prescription
-
Double vision in one eye due to lens irregularities
-
Reduced contrast sensitivity, affecting mobility and independence
Clinical Signs
-
Lens opacity visible on slit-lamp examination
-
Decreased red reflex
-
Reduced visual acuity uncorrectable by glasses
-
Dense nuclear sclerosis or cortical changes
-
Coexisting signs of glaucoma or macular disease
-
Poor contrast and brightness perception during testing
These symptoms and signs confirm the need for cataract surgery using phacoemulsification and foldable IOL implantation.
Diagnosis of Conditions Requiring Phaco With Foldable IOL
Diagnosis is based on a complete ophthalmic evaluation including:
Ophthalmic Assessments
-
Visual acuity testing (distance, near, pinhole)
-
Slit-lamp examination to evaluate cataract type and severity
-
Dilated fundus exam to assess retina and optic nerve
-
Tonometry for intraocular pressure
-
Contrast sensitivity testing in advanced cases
Biometry & Measurements
-
Axial length measurement (optical or ultrasound biometry)
-
Keratometry for corneal curvature
-
IOL power calculation using modern formulas
-
Endothelial cell count to evaluate corneal health
-
Anterior chamber depth assessment
Systemic Evaluation
-
Diabetic status, blood pressure, cardiovascular condition
-
Current medications
Accurate diagnostics ensure optimal IOL selection, proper surgical planning, and better postoperative outcomes.
Treatment Options of Phaco With Foldable IOL
Surgical Procedure Overview
The phacoemulsification with foldable IOL implantation includes:
-
Topical anesthesia
-
Micro-incision at the corneal limbus
-
Capsulorhexis (creating a circular opening)
-
Hydrodissection to separate lens from capsule
-
Phacoemulsification of the nucleus into fragments
-
Aspiration of cortical material
-
Insertion of foldable IOL using injector systems
-
Self-sealing wound closure with no sutures
Types of Foldable IOLs
-
Monofocal IOLs: Correct distance vision
-
Multifocal IOLs: Provide distance and near vision
-
Toric IOLs: Correct astigmatism
-
Extended-Depth-of-Focus (EDoF) IOLs: Increase the range of clear vision
-
Accommodating IOLs: Mimic natural focusing ability
Advanced Approaches
-
Femtosecond laser-assisted cataract surgery (FLACS)
-
Micro-incision cataract surgery (MICS)
-
Premium lens implants for enhanced spectacle independence
Prevention and Management of Conditions Requiring Phaco With Foldable IOL
Preventive Strategies
-
UV protection using sunglasses
-
Blood sugar control in diabetics
-
Nutrient-rich diet containing antioxidants
-
Avoidance of smoking and excessive alcohol
-
Regular eye check-ups, especially after age 50
Perioperative Management
-
Preoperative antibiotics to prevent infection
-
Optimizing systemic health
-
Ocular surface preparation for better healing
-
Patient education regarding postoperative care
Postoperative Management
-
Antibiotic and anti-inflammatory drops
-
Avoidance of rubbing the eye, heavy lifting, or water exposure
-
Regular follow-up visits to monitor healing
-
Early detection of complications like inflammation, infection, or elevated IOP
Complications of Phaco With Foldable IOL
While complications are rare, they may include:
Intraoperative
-
Posterior capsule rupture
-
Zonular weakness
-
Dropped nucleus
-
Iris trauma
Early Postoperative
-
Corneal edema
-
Elevated intraocular pressure
-
Inflammatory reactions
-
Wound leak
-
Infection (endophthalmitis - rare but serious)
Late Complications
-
Posterior capsular opacification (PCO)
-
IOL decentration or dislocation
-
Cystoid macular edema
-
Retinal detachment
-
Glare, halos, or visual disturbances
Prompt treatment helps preserve visual outcomes.
Living with the Condition After Phaco With Foldable IOL
Post-Surgery Experience
Most patients experience dramatic improvement in vision within 24-48 hours. Colors appear brighter, objects look sharper, and glare decreases significantly. Many patients regain independence in daily activities.
Rehabilitation & Recovery
-
Use eye drops as prescribed
-
Avoid strenuous activities for 1-2 weeks
-
Protect eyes from dust and injury
-
Follow-up appointments to track healing
Long-Term Expectations
-
Clear, stable vision
-
Possible freedom from glasses depending on the IOL chosen
-
Periodic monitoring for late complications
-
Better mobility, safety, and overall quality of life
Top 10 Frequently Asked Questions about Phacoemulsification With Foldable IOL
1. What is phacoemulsification with foldable IOL, and how does it differ from traditional cataract surgery?
Phacoemulsification with foldable intraocular lens (IOL) is a minimally invasive, modern technique for cataract removal. Cataracts occur when the natural lens becomes cloudy due to aging, trauma, or systemic conditions like diabetes. In phacoemulsification:
-
A tiny 2-3 mm corneal incision is made, much smaller than the 10-12 mm incision used in traditional extracapsular cataract surgery.
-
A high-frequency ultrasonic probe emulsifies the cloudy lens, turning it into microscopic pieces that are suctioned out.
-
A foldable IOL is inserted through the same small incision and unfolds within the eye to restore clarity.
Compared to traditional methods, phacoemulsification reduces surgical trauma, minimizes post-operative astigmatism, accelerates recovery, and allows for premium IOL implantation, providing both functional and cosmetic benefits.
2. Why is phacoemulsification with foldable IOL performed?
Phacoemulsification with foldable IOL is performed when cataracts significantly impair vision or threaten quality of life. Indications include:
-
Blurry, cloudy, or dim vision that hinders daily activities like reading, driving, or working
-
Increased glare, halos, and poor night vision
-
Cataract complications, such as secondary glaucoma, lens-induced uveitis, or phacomorphic glaucoma
-
Desire for long-term vision correction using advanced foldable IOLs that also correct astigmatism or presbyopia
The procedure restores clear vision, reduces dependence on glasses, and improves visual quality, allowing patients to resume daily activities safely.
3. Who is an ideal candidate for phacoemulsification with foldable IOL?
Candidates include:
-
Adults or elderly patients with clinically significant cataracts affecting vision
-
Individuals with healthy corneal and retinal structures, as these determine visual outcomes
-
Patients seeking minimally invasive surgery with faster recovery
-
Those desiring simultaneous correction of refractive errors with premium foldable IOLs
-
Patients without active eye infections or uncontrolled systemic conditions like severe hypertension or diabetes
Comprehensive preoperative evaluation involves visual acuity tests, slit-lamp examination, corneal topography, biometry for IOL power calculation, and ocular health assessment.
4. How is phacoemulsification with foldable IOL performed? Step-by-step procedure
-
Anesthesia: Topical or local anesthesia is administered; sedation may be given for anxious patients.
-
Incision: A 2-3 mm corneal incision is made at the periphery.
-
Capsulorhexis: A circular opening in the anterior lens capsule allows access to the cataract.
-
Phacoemulsification: Ultrasound energy breaks the lens into tiny fragments, which are suctioned out.
-
IOL implantation: The foldable IOL is inserted through the same incision and unfolds in the capsular bag.
-
Closure: Incision is usually self-sealing; protective shield may be applied.
The surgery typically takes 15-30 minutes, and most patients are discharged the same day. Recovery is rapid, with minimal discomfort and early visual improvement.
5. What types of foldable IOLs are available, and how do they benefit patients?
Foldable IOLs come in several varieties:
-
Monofocal IOLs: Provide clear vision at one distance (usually far); glasses may be needed for near work
-
Multifocal IOLs: Offer clear vision at near, intermediate, and far distances, reducing dependency on glasses
-
Toric IOLs: Correct astigmatism for sharper vision
-
Accommodating IOLs: Adjust focus for near and far vision, mimicking the natural lens
Advantages of foldable IOLs:
-
Smaller incision → faster healing and less astigmatism
-
Long-lasting clarity and structural stability
-
Compatibility with premium designs to improve quality of vision
-
Safe and effective for both cataract removal and refractive correction
Foldable IOLs provide superior outcomes compared to rigid lenses, particularly in terms of visual acuity, cosmetic appearance, and patient satisfaction.
6. Is phacoemulsification with foldable IOL painful?
-
During surgery: Local or topical anesthesia ensures no pain; patients may feel pressure or vibration but no discomfort
-
After surgery: Mild soreness, burning, or irritation may occur at the incision site
-
Temporary symptoms: Light sensitivity, tearing, or mild foreign body sensation is common
-
Pain is typically mild and managed with eye drops or oral analgesics, resolving within a few days.
Patients generally report rapid comfort and noticeable vision improvement within 24-48 hours.
7. What are the risks and potential complications of phaco with foldable IOL?
Although very safe, potential complications include:
-
Endophthalmitis (eye infection) - rare but serious
-
Posterior capsule rupture
-
Corneal edema or temporary clouding
-
IOL dislocation, tilt, or decentration
-
Secondary cataract (posterior capsule opacification) - treatable with YAG laser
-
Rare complications: retinal detachment, macular edema, glaucoma, or visual distortion
Modern surgical techniques and sterile protocols keep complication rates extremely low.
8. What is the recovery process after phacoemulsification with foldable IOL?
-
Hospital stay: Usually outpatient; discharge same day
-
Protection: Eye shield for 24-48 hours; avoid rubbing the eye
-
Medication: Antibiotic and anti-inflammatory eye drops for 2-4 weeks
-
Activity: Avoid swimming, heavy lifting, or dusty environments for 2-4 weeks
-
Follow-up visits: 1 day, 1 week, and 4-6 weeks post-surgery
Patients often experience functional vision within 24-48 hours, with optimal clarity and stabilization achieved over several weeks.
9. How successful is phacoemulsification with foldable IOL?
-
Success rate >95% for restoring clear, functional vision
-
Most patients achieve 20/40 vision or better
-
Immediate visual improvement is often noticeable, with full recovery over weeks
-
Premium IOLs can correct refractive errors, reducing the need for glasses
-
Rare complications are usually manageable, and long-term outcomes are excellent
Phacoemulsification with foldable IOL provides reliable, long-lasting visual restoration.
10. How much does phacoemulsification with foldable IOL cost, and is it covered by insurance?
Costs vary depending on:
-
Surgeon and hospital fees
-
Type of IOL (standard monofocal vs. premium multifocal or toric lenses)
-
Anesthesia and operating room charges
-
Post-operative care, medications, and follow-up
Standard cataract surgery with foldable IOL is medically necessary and usually covered by insurance. Premium or cosmetic lenses may require additional out-of-pocket payment. Patients should confirm coverage, co-pays, and expected expenses with their provider before surgery.


