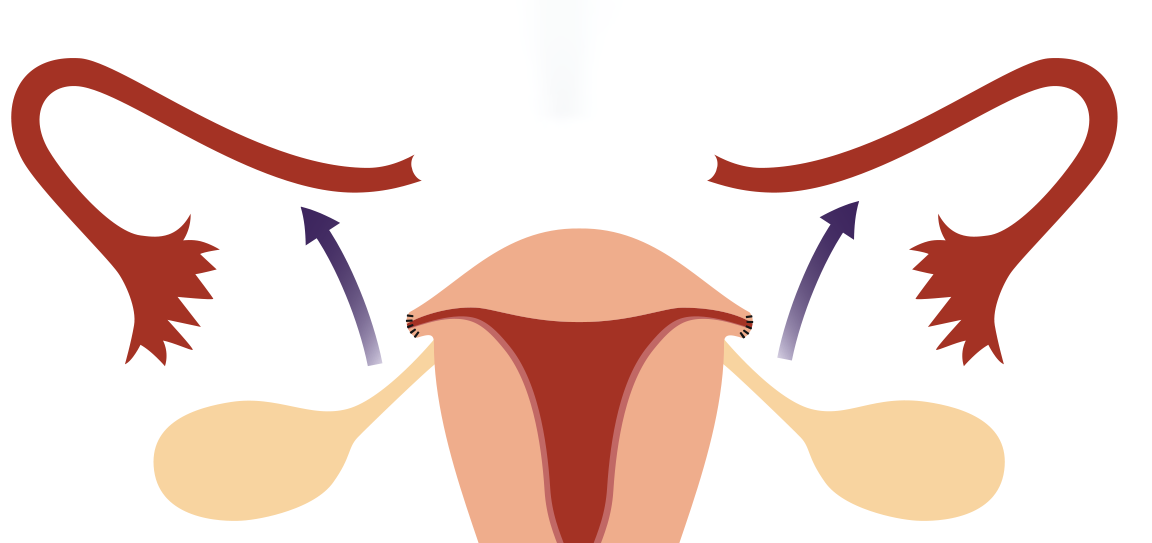
Introduction to Salpingo-Oophorectomy
Salpingo-oophorectomy is a surgical procedure in which one or both ovaries and their corresponding fallopian tubes are removed. The term “salpingo” refers to the fallopian tube, and “oophorectomy” refers to the removal of the ovaries. Depending on the clinical condition, this procedure may be performed unilaterally (removal of one ovary and fallopian tube) or bilaterally (removal of both). The procedure is often recommended when there are serious medical conditions affecting the ovaries or fallopian tubes, including cancer, tumors, cysts, endometriosis, or ovarian torsion. In some cases, it is performed as a preventive measure in individuals at high risk for ovarian or related cancers, such as those with a family history or certain genetic mutations like BRCA1 or BRCA2.
Salpingo-oophorectomy can be done through minimally invasive laparoscopic surgery, which is the most common method today due to its advantages in terms of smaller incisions, quicker recovery times, and less postoperative pain. Alternatively, it can be done via open surgery (laparotomy) in more complex cases. While this procedure provides significant therapeutic benefits, particularly in terms of preventing or treating cancer, it also comes with long-term consequences related to fertility, hormonal changes, and overall well-being. For women of childbearing age, the removal of both ovaries leads to infertility and the sudden onset of menopause, with all the associated symptoms like hot flashes, mood swings, and vaginal dryness.
This article will discuss the various causes and indications for salpingo-oophorectomy, the types of surgeries available, the potential risks and complications, the recovery process, and the emotional and physical implications of undergoing this procedure. Understanding the full scope of salpingo-oophorectomy is essential for individuals making informed decisions about their health and surgical options.
Causes and Risk Factors for Salpingo-Oophorectomy
Salpingo-Oophorectomy is typically performed in response to various health conditions that affect the ovaries and fallopian tubes. Below are the common causes and risk factors:
Benign Ovarian Conditions
-
Ovarian cysts and tumors: These are fluid-filled sacs or growths that develop on or in the ovaries. While many cysts are benign and resolve on their own, persistent or large cysts can cause pain, rupturing, or torsion (twisting), and may require removal of the affected ovary and tube.
-
Endometriosis: This condition occurs when tissue similar to the uterine lining grows outside the uterus, often affecting the ovaries. It can cause cysts known as endometriomas, which may need to be surgically removed.
Pelvic Infections
-
Tubo-ovarian abscess: This is an infection that can lead to an abscess or collection of pus in the fallopian tubes or ovaries, often due to pelvic inflammatory disease (PID). If left untreated, this infection can lead to severe complications, requiring removal of the infected ovary and tube.
Cancer or Risk of Cancer
-
Ovarian cancer: One of the most significant reasons for performing a Salpingo-Oophorectomy is the presence of ovarian cancer or a strong suspicion of it. This surgery is performed as part of cancer treatment or as a preventive measure in women with genetic predispositions.
-
Prophylactic surgery: Women who are at high risk of ovarian cancer, especially those with mutations in the BRCA1 or BRCA2 genes, may opt for Salpingo-Oophorectomy to reduce the risk of cancer.
Genetic and Family History
-
Women with a family history of ovarian or breast cancer, or those who carry genetic mutations (e.g., BRCA1 or BRCA2) that increase their cancer risk, may choose to undergo Salpingo-Oophorectomy as a preventive measure. This surgery can significantly lower the risk of developing ovarian cancer.
Chronic Pelvic Pain or Fertility Issues
-
In cases of severe, unrelenting pelvic pain due to ovarian pathology or tubal issues that cannot be managed with medication, surgery may be recommended to remove the affected organs.
-
Additionally, women who have failed to conceive due to ovarian or tubal dysfunction might undergo the procedure to address infertility issues.
Symptoms and Signs Indicating the Need for Salpingo-Oophorectomy
The need for Salpingo-Oophorectomy typically arises when symptoms become unmanageable or when diagnostic tests reveal underlying conditions that could be improved or mitigated with surgery. Common signs that may indicate the need for this surgery include:
Pelvic Pain
Chronic pelvic pain is one of the most common symptoms that lead to Salpingo-Oophorectomy. This pain can result from ovarian cysts, tumors, or endometriosis. The pain may be constant or may worsen during menstruation or sexual intercourse.
Abdominal Distension or Swelling
Women with large ovarian cysts or tumors may experience bloating or visible swelling in the abdomen. This can be due to the size of the mass putting pressure on surrounding organs.
Irregular Menstrual Cycles or Abnormal Bleeding
If ovarian or uterine conditions like cysts, fibroids, or tumors are present, they can disrupt regular menstruation, leading to heavy bleeding, irregular cycles, or prolonged periods. In some cases, abnormal bleeding may indicate a more serious underlying condition, such as cancer.
Infertility
In cases where the ovaries or fallopian tubes are significantly affected by conditions like endometriosis, pelvic infections, or cysts, fertility may be compromised. If fertility preservation is not an option or if the patient has completed childbearing, Salpingo-Oophorectomy may be performed to address the issue.
Masses or Tumors Detected
The presence of an ovarian mass or tumor, especially if it is suspected to be malignant, is often detected through imaging or physical exams. In such cases, surgery may be recommended to remove the mass and prevent further complications.
Symptoms of Ovarian Cancer
For patients with risk factors for ovarian cancer or those who exhibit suspicious symptoms such as abdominal bloating, difficulty eating, pelvic discomfort, and changes in bowel movements, Salpingo-Oophorectomy may be performed as a diagnostic or therapeutic measure.
Diagnosis of Conditions Leading to Salpingo-Oophorectomy
The diagnosis of conditions requiring Salpingo-Oophorectomy is primarily made through a combination of patient history, clinical examination, and imaging studies. The following diagnostic tools are typically employed:
Pelvic Ultrasound
A pelvic ultrasound is a non-invasive imaging technique commonly used to assess ovarian cysts, masses, or tumors. This method can help determine the size, location, and nature (solid or fluid-filled) of ovarian growths.
CT Scan or MRI
For larger masses or when malignancy is suspected, a CT scan or MRI may be performed to get a more detailed view of the ovaries, fallopian tubes, and surrounding structures. These scans can provide information about the extent of the disease, if cancer is suspected.
Blood Tests
Blood tests to check for tumor markers like CA-125 (used in ovarian cancer diagnosis), liver function, and kidney function help provide more clarity about the nature of the tumor or cyst. These tests also assist in preoperative preparation.
Laparoscopy
In certain cases, a diagnostic laparoscopy may be performed to visualize the pelvic organs and gather tissue samples. This minimally invasive procedure allows surgeons to get a clearer picture of the extent of the disease, especially if cancer is suspected.
Genetic Testing
For women with a strong family history of ovarian or breast cancer, genetic testing (for BRCA1 or BRCA2 mutations) may be recommended. This helps assess whether the individual is at high risk for developing ovarian cancer and guides the decision-making process regarding preventive surgery.
Treatment Options for Salpingo-Oophorectomy
The treatment option for Salpingo-Oophorectomy primarily depends on the underlying reason for the surgery, the patient's reproductive desires, and other individual factors. The two main approaches are:
Unilateral Salpingo-Oophorectomy
This surgery involves the removal of one ovary and its corresponding fallopian tube. This procedure may be performed in cases where only one ovary is affected by a condition such as a cyst, endometriosis, or a benign tumor. The remaining ovary can continue to produce hormones, and the woman may still retain fertility.
Bilateral Salpingo-Oophorectomy (BSO)
In some cases, both ovaries and fallopian tubes are removed. This is often the case for women with a higher risk of ovarian cancer, those who have completed their family planning, or women who have malignancy or recurrent disease in both ovaries. A BSO will result in the woman entering surgical menopause immediately if the uterus is intact.
Minimally Invasive Techniques
Modern Salpingo-Oophorectomy is increasingly performed using laparoscopic surgery (keyhole surgery), which involves smaller incisions, reduced scarring, faster recovery times, and less postoperative pain compared to traditional open surgery.
Hormone Replacement Therapy (HRT)
If both ovaries are removed in premenopausal women, hormone replacement therapy is often recommended to replace the hormones no longer produced by the ovaries. This helps alleviate symptoms of menopause, such as hot flashes, night sweats, vaginal dryness, and bone thinning.
Prevention and Management of Salpingo-Oophorectomy
While Salpingo-Oophorectomy may be necessary in certain medical conditions, preventive strategies can reduce the need for surgery in the first place.
Genetic Counseling and Risk Reduction
For women with a family history of ovarian cancer or genetic mutations (such as BRCA1 or BRCA2), preventive Salpingo-Oophorectomy may be considered. Genetic counseling is essential for understanding risks and making informed decisions about surgery.
Prophylactic Measures
In women at high risk of developing ovarian cancer, the removal of both ovaries and fallopian tubes after childbearing is complete is often recommended as a preventive measure to reduce cancer risk.
Lifestyle Modifications
Maintaining a healthy diet, exercising regularly, and avoiding smoking can help reduce the risk of many gynecologic diseases, including ovarian cancer. Additionally, maintaining a healthy weight can decrease the risk of ovarian cysts and other related conditions.
Complications of Salpingo-Oophorectomy
Although Salpingo-Oophorectomy is generally safe, there are some risks and potential complications that can arise:
-
Infection: As with any surgery, infection is a risk, especially if proper care isn't taken after the procedure.
-
Bleeding: Post-operative bleeding is another potential complication, though it is rare with laparoscopic procedures.
-
Premature Menopause: If both ovaries are removed, the patient will experience menopause immediately, which can cause symptoms such as hot flashes, vaginal dryness, and osteoporosis.
-
Hormonal Imbalances: The removal of the ovaries leads to a lack of estrogen and progesterone, which can affect mood, bone density, and cardiovascular health.
-
Surgical Complications: These include damage to surrounding organs, such as the bladder or intestines, and blood clots.
Living with the Condition After Salpingo-Oophorectomy
Life after Salpingo-Oophorectomy depends on the type of surgery performed (unilateral vs. bilateral) and the patient's overall health.
Recovery and Postoperative Care
Patients who undergo Salpingo-Oophorectomy typically recover within a few weeks, with most able to return to normal activities within 4 to 6 weeks, depending on whether the procedure was laparoscopic or open. Postoperative care includes rest, pain management, and follow-up visits to monitor recovery.
Managing Hormonal Changes
If both ovaries are removed, women will immediately experience menopause. Hormone replacement therapy (HRT) is often recommended to manage menopause symptoms, although it requires careful monitoring for long-term health risks.
Emotional Wellbeing
It is important to address emotional and psychological impacts, particularly for younger women who may experience feelings of loss due to the removal of the ovaries, especially if they had future fertility plans.
Long-term Health Monitoring
Women who have undergone Salpingo-Oophorectomy should continue to monitor their overall health, particularly regarding bone density, cardiovascular health, and maintaining a healthy lifestyle to manage the risks associated with hormone loss.
Top 10 Frequently Asked Questions about Salpingo-Oophorectomy
1. What is a salpingo-oophorectomy?
A salpingo-oophorectomy is a surgical procedure in which one or both of a woman's ovaries and fallopian tubes are removed. This procedure can be either unilateral (removal of one ovary and one fallopian tube) or bilateral (removal of both ovaries and both fallopian tubes). It is typically performed to treat conditions such as ovarian cancer, fallopian tube cancer, endometriosis, ectopic pregnancy, or ovarian cysts. The procedure can also be performed as a preventive measure in women at high risk for ovarian cancer, such as those with a BRCA gene mutation.
2. Why is a salpingo-oophorectomy performed?
Salpingo-oophorectomy is performed for several reasons, including:
-
Ovarian cancer: If cancer is found in the ovaries or fallopian tubes, removal of these organs is often necessary.
-
Benign ovarian conditions: Such as ovarian cysts, endometriosis, or fibroids that don't respond to other treatments.
-
Ectopic pregnancy: If a pregnancy implants in the fallopian tube, it can be life-threatening, and the tube needs to be removed.
-
Genetic risk: Women with a strong family history of ovarian cancer or BRCA gene mutations may opt for prophylactic removal of the ovaries and fallopian tubes to reduce their cancer risk.
In some cases, preventive salpingo-oophorectomy is done to lower the risk of developing breast cancer or ovarian cancer in women with high genetic risks.
3. What are the different types of salpingo-oophorectomy?
There are two main types of salpingo-oophorectomy:
-
Unilateral Salpingo-Oophorectomy: Involves the removal of one ovary and one fallopian tube, often performed when one side is affected by a disease, such as ovarian cysts, endometriosis, or an ectopic pregnancy.
-
Bilateral Salpingo-Oophorectomy: Involves the removal of both ovaries and fallopian tubes. This is often done in cases of ovarian cancer, high genetic risk for cancer, or when both ovaries are severely affected by disease. Bilateral removal leads to immediate menopause if the woman has not already reached menopause.
4. How is salpingo-oophorectomy performed?
Salpingo-oophorectomy is typically performed under general anesthesia, and the procedure may be done using one of the following techniques:
-
Laparoscopic Surgery: This minimally invasive technique involves several small incisions through which a camera and surgical instruments are inserted to remove the ovaries and fallopian tubes. This results in smaller scars, less pain, and faster recovery.
-
Open Surgery (Laparotomy): This is a more invasive approach that requires a larger incision in the abdomen to access the ovaries and fallopian tubes. It is typically used for more complex cases, such as when cancer is present or when laparoscopic surgery is not feasible.
In both methods, the surgeon removes the affected organs and checks for any signs of disease or cancer spread.
5. What are the risks and potential complications of salpingo-oophorectomy?
As with any surgery, salpingo-oophorectomy carries some risks:
-
Infection: A risk with any surgical procedure, particularly if the surgical site is not properly cared for.
-
Bleeding: There is a small risk of significant bleeding, which could require a blood transfusion.
-
Damage to surrounding organs: The ovaries and fallopian tubes are located near other organs, such as the bladder and intestines, and there is a small risk of accidental injury to these organs during surgery.
-
Early menopause: If both ovaries are removed, a woman will experience immediate menopause, leading to symptoms like hot flashes, night sweats, vaginal dryness, and potential long-term health risks like osteoporosis and heart disease.
-
Hormonal imbalances: Even if only one ovary is removed, hormonal imbalances can occur, particularly if the remaining ovary is not able to compensate for the loss.
6. What can I expect during recovery after salpingo-oophorectomy?
Recovery after salpingo-oophorectomy depends on the type of surgery performed:
-
Laparoscopic Surgery: Recovery is generally quicker, with most women able to return to normal activities within 1-2 weeks, although full recovery may take 3-4 weeks.
-
Open Surgery: Recovery is more gradual, with a typical hospital stay of 3-5 days and a recovery period of 6-8 weeks before resuming strenuous activities.
After surgery, you will be given pain relief medication, and you should follow the surgeon's instructions for wound care and activity restrictions. It is common to experience abdominal discomfort, bloating, or tenderness in the first few days.
7. Will salpingo-oophorectomy affect my fertility?
If only one ovary and one fallopian tube are removed (unilateral salpingo-oophorectomy), you can still become pregnant using the remaining ovary and fallopian tube, although fertility may be slightly reduced depending on the overall health of the reproductive system.
However, if both ovaries are removed (bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy), fertility is permanently lost because there are no ovaries to produce eggs. In such cases, women may explore fertility preservation options such as egg freezing before surgery if they wish to have biological children in the future.
8. How does salpingo-oophorectomy affect menopause?
Bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy induces surgical menopause in women who have not already reached menopause. Removing both ovaries causes an immediate drop in the production of estrogen and progesterone, hormones that regulate menstrual cycles and fertility. This leads to menopausal symptoms such as:
-
Hot flashes
-
Night sweats
-
Mood swings
-
Vaginal dryness
-
Sleep disturbances
Women undergoing this procedure may need hormone replacement therapy (HRT) to manage these symptoms and reduce the long-term risk of osteoporosis and heart disease. If only one ovary is removed, menopause may occur later, but some women experience changes in their menstrual cycle or early menopause.
9. What is the difference between a salpingo-oophorectomy and a hysterectomy?
While both procedures involve the removal of reproductive organs, they differ in what is removed:
-
Salpingo-oophorectomy involves the removal of the ovaries and fallopian tubes, but the uterus is left intact.
-
Hysterectomy involves the removal of the uterus, and depending on the type of hysterectomy, it may also include the ovaries and fallopian tubes.
In cases where both the uterus and ovaries are removed, the procedure is known as a total hysterectomy with bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy.
10. How can I prepare for salpingo-oophorectomy surgery?
To prepare for salpingo-oophorectomy, you should:
-
Have a thorough consultation with your surgeon to discuss the risks, benefits, and alternatives to the surgery.
-
Undergo pre-operative tests, including blood work, imaging tests, and possibly an EKG or chest X-ray to assess your overall health.
-
Stop taking certain medications, such as blood thinners, as directed by your doctor.
-
Arrange for someone to drive you home after the surgery and assist you during your recovery, as you may be unable to drive for a short time.
-
Follow any fasting instructions for the day of surgery, as eating or drinking too close to surgery can cause complications.


