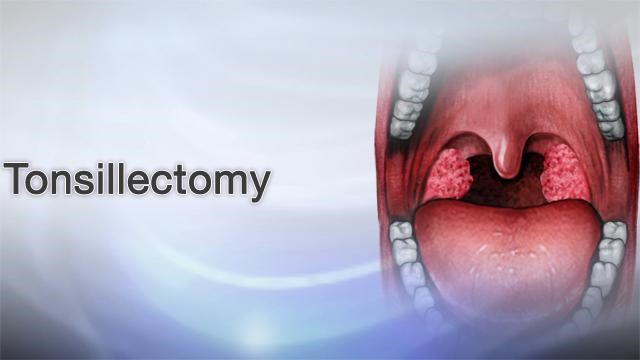
Introduction to Tonsillectomy (Adult)
Tonsillectomy (Adult) is a surgical procedure that involves the removal of the tonsils, which are two small lymphoid tissues located at the back of the throat. While tonsillectomy is commonly performed in children, adults may also require this surgery, usually due to recurrent tonsillitis, chronic tonsil infections, obstructive sleep apnea, difficulty swallowing, or other complications such as peritonsillar abscesses.
The procedure is typically performed under general anesthesia, and the surgeon removes the tonsils through the mouth without any external incisions. In adults, recovery can be slightly longer and more uncomfortable compared to children, with throat pain, difficulty swallowing, and mild bleeding being common post-operative symptoms. Pain management, hydration, and soft diet are essential during the recovery period, which generally lasts about 1-2 weeks.
Tonsillectomy in adults not only helps in reducing the frequency of throat infections but can also improve breathing, sleep quality, and overall quality of life. The decision to perform the surgery is carefully considered based on medical history, severity of symptoms, and response to other treatments.
Causes and Risk Factors of Tonsillectomy (Adult)
Tonsillectomy is usually not a first-line treatment for adults. It is considered when repeated infections, obstructive symptoms, or complications make the tonsils a source of health issues.
Primary Causes
-
Chronic or Recurrent Tonsillitis
-
Recurrent infections, often more than five episodes per year, characterized by sore throat, fever, and swelling.
-
-
Peritonsillar Abscess (Quinsy)
-
Accumulation of pus near the tonsils, causing severe throat pain, difficulty swallowing, and in some cases, airway obstruction.
-
-
Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA)
-
Enlarged tonsils can block the airway during sleep, leading to snoring, daytime fatigue, and low blood oxygen levels.
-
-
Tonsil Stones (Tonsilloliths)
-
Calcified debris that can cause halitosis, throat discomfort, and repeated infections.
-
-
Suspicion of Cancer
-
Unilateral enlargement, persistent lesions, or abnormal appearance of the tonsils may indicate malignancy.
-
Risk Factors
-
Age: Adults have higher post-operative risks than children.
-
Smoking: Increases risk of infection and delays healing.
-
Obesity: Exacerbates sleep apnea and complicates anesthesia.
-
Immune System Disorders: Conditions such as diabetes or immunodeficiency increase infection risk.
-
Previous Tonsillar Surgery: Scar tissue may complicate the procedure.
Symptoms and Signs Indicating Tonsillectomy (Adult)
Tonsillectomy is considered when symptoms significantly affect daily life or pose a health risk.
Common Symptoms
-
Frequent Sore Throat: Persistent throat pain and swelling.
-
Difficulty Swallowing (Dysphagia): Pain or obstruction while eating or drinking.
-
Halitosis: Chronic bad breath often caused by tonsil stones or infections.
-
Obstructive Symptoms: Snoring, choking, or apnea during sleep.
-
Ear Pain: Referred pain due to shared nerve pathways.
-
Fever and Fatigue: Systemic symptoms resulting from recurrent infections.
Red Flags
-
Difficulty breathing
-
Severe pain not relieved by medications
-
Bleeding from the tonsils
-
Unilateral tonsil enlargement suggesting malignancy
Diagnosis of Tonsillectomy (Adult)
Before recommending surgery, doctors conduct a thorough evaluation to assess the severity and frequency of symptoms and rule out other causes.
Diagnostic Steps
-
Medical History: Documenting infection frequency, prior treatments, and sleep disturbances.
-
Physical Examination: Visual inspection and palpation of tonsils for size, inflammation, and asymmetry.
-
Throat Swab and Culture: Identifying bacterial infections, such as Streptococcus pyogenes.
-
Blood Tests: Complete blood count (CBC) to assess systemic infection; immunodeficiency tests if recurrent infections occur.
-
Imaging Studies: CT or MRI for suspected abscesses or malignancy.
-
Sleep Study (Polysomnography): Recommended if sleep apnea is suspected.
-
Tonsil Size Grading: Scale of 1-4 used to evaluate obstruction severity.
Treatment Options of Tonsillectomy (Adult)
Non-Surgical Management
Before surgery, doctors may attempt conservative treatments:
-
Antibiotics: For bacterial infections.
-
Anti-inflammatory medications: Reduce pain and swelling.
-
Saltwater gargles: Provide symptomatic relief.
-
Hydration and rest: Support immune recovery.
Surgical Procedure
Tonsillectomy is usually performed under general anesthesia in adults. Common surgical techniques include:
-
Cold Knife (Steel) Tonsillectomy: Traditional scalpel method.
-
Electrocautery: Burns tissue to remove tonsils and control bleeding.
-
Laser Tonsillectomy: Precision removal using laser energy.
-
Coblation: Uses radiofrequency energy in saline to remove tissue at lower temperatures, reducing post-operative pain.
Post-Surgical Recovery
-
Pain management is essential, including acetaminophen or NSAIDs.
-
Recovery usually takes 10-14 days, longer than in children.
-
Adequate hydration and soft diet recommended.
-
Follow-up appointments monitor healing and prevent complications.
Prevention and Management of Tonsillectomy (Adult)
Before Surgery
-
Maintain oral hygiene to reduce bacterial load.
-
Avoid smoking and alcohol.
-
Treat infections promptly with antibiotics.
After Surgery
-
Hydration and Diet: Soft, cold foods are preferable.
-
Pain Management: As prescribed by the surgeon.
-
Activity Restrictions: Avoid heavy lifting and strenuous activity for at least 2-3 weeks.
-
Monitor for Bleeding: Seek immediate care if any post-operative bleeding occurs.
Complications of Tonsillectomy (Adult)
Although generally safe, adult tonsillectomy carries higher risk of complications than in children:
-
Bleeding (Hemorrhage): Can occur immediately or several days post-surgery.
-
Severe Pain: More intense than in pediatric cases.
-
Infection: Rare, but possible in the post-operative period.
-
Changes in Taste: Temporary alteration of taste perception.
-
Dehydration: Pain may limit oral intake.
-
Anesthesia Risks: Adults with comorbidities have slightly higher risk.
Living with the Condition Post-Tonsillectomy
Recovery
-
Expect 10-14 days for full recovery.
-
Gradually resume work or daily activities.
-
Pain and fatigue are normal; rest is essential.
Long-Term Health
-
Most adults experience fewer throat infections post-surgery.
-
Sleep quality often improves in cases of obstructive sleep apnea.
-
Regular follow-up ensures proper healing and checks for rare complications.
Lifestyle Tips
-
Maintain hydration and good oral hygiene.
-
Avoid smoking and alcohol during recovery.
-
Eat soft foods until swallowing becomes comfortable.
-
Monitor for fever, bleeding, or persistent pain and seek medical attention if they occur.
Top 10 Frequently Asked Questions about Tonsillectomy in Adults
1. What is a tonsillectomy in adults?
A tonsillectomy is a surgical procedure to remove the tonsils, which are two small glands located at the back of the throat. In adults, it is usually performed to treat chronic tonsillitis, recurrent throat infections, sleep apnea, or enlarged tonsils causing difficulty swallowing or breathing.
2. Why might an adult need a tonsillectomy?
Adults may need a tonsillectomy if they experience:
-
Recurrent or chronic tonsillitis (frequent throat infections)
-
Difficulty swallowing or persistent throat pain
-
Sleep-disordered breathing or obstructive sleep apnea
-
Tonsil stones causing bad breath or discomfort
-
Suspicion of tumors or growths on the tonsils
3. How is a tonsillectomy performed in adults?
The surgery is usually done under general anesthesia. The tonsils are removed using one of several techniques: scalpel, electrocautery (heat), laser, or radiofrequency. The procedure typically takes 30-60 minutes. Adults may have slightly longer recovery than children.
4. What should I do to prepare for adult tonsillectomy?
Preparation steps often include:
-
Avoiding food and drinks 6-8 hours before surgery
-
Informing your doctor about medications or supplements
-
Arranging transportation home after the procedure
-
Stopping smoking, which can slow healing
-
Discussing any pre-existing conditions like heart or lung disease
5. What is the recovery time after a tonsillectomy in adults?
Recovery usually takes 10-14 days, but adults may experience discomfort for up to 2-3 weeks. Pain, difficulty swallowing, and mild fever are common during the first week. Soft foods, plenty of fluids, and rest help speed up recovery.
6. What are the common risks and complications in adult tonsillectomy?
While generally safe, risks include:
-
Bleeding (primary or secondary)
-
Infection at the surgical site
-
Pain in the throat, ears, or jaw
-
Swelling causing breathing difficulty
-
Reactions to anesthesia
7. How is pain managed after adult tonsillectomy?
Pain can be managed with:
-
Prescribed painkillers (acetaminophen or opioids)
-
Ice packs or throat lozenges
-
Drinking cold fluids and eating soft foods
-
Avoiding acidic, spicy, or rough foods that can irritate the throat
8. Are there dietary restrictions after adult tonsillectomy?
Yes, adults are advised to eat soft, easy-to-swallow foods such as:
-
Yogurt, applesauce, pudding, mashed potatoes
-
Cold or lukewarm soups
-
Avoiding spicy, acidic, or crunchy foods that may irritate the surgical site
-
Staying hydrated to prevent throat dryness
9. When should I contact my doctor after a tonsillectomy?
Seek medical attention if you experience:
-
Severe or persistent bleeding
-
Difficulty breathing or swallowing
-
High fever or signs of infection
-
Severe pain not relieved by medications
-
Dehydration or inability to eat or drink
10. What are the long-term benefits of adult tonsillectomy?
Adults often experience:
-
Fewer throat infections
-
Improved sleep quality and reduced snoring
-
Relief from chronic throat pain or discomfort
-
Reduced risk of tonsil stones
-
Overall improvement in quality of life


